Why Pimping Works: The Neurophysiology of Emotional Memories
- PMID: 39130900
- PMCID: PMC11313157
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.64237
Why Pimping Works: The Neurophysiology of Emotional Memories
Abstract
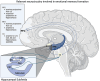
A time-honored medical ritual that combines emotion and cognition into a seamless consolidation of lucid memories is a feared teaching method in medical education. The resulting neurophysiology is explained from a neurosurgeon's perspective - equal parts guilt and dread as a prescription for an improved and sustained trainee fund of knowledge. Much of the available literature published with regard to pimping explores its pedagogy and use in medical practice. This review aims to explore the neurobehavioral and biological aspects of pimping in why it remains a popular teaching model. We describe the neuromodulatory process of integrating emotions and memory as observed during pimping. Additionally, we explore the neuronal pathways and circuits involved in memory encoding, consolidation, and retrieval. Finally, we explored the effects of this methodology as it is currently used in the United States medical education system.
Keywords: emotional memory; hippocampus; learning; neurophysiology; pimping.
Copyright © 2024, Jimenez et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pimping in Residency: The Emotional Roller-Coaster of a Pedagogical Method - A Qualitative Study Using Interviews and Rich Picture Drawings.Teach Learn Med. 2019 Oct-Dec;31(5):497-505. doi: 10.1080/10401334.2019.1610658. Epub 2019 May 13. Teach Learn Med. 2019. PMID: 31084222
-
Socrates was not a pimp: changing the paradigm of questioning in medical education.Acad Med. 2015 Jan;90(1):20-4. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000000446. Acad Med. 2015. PMID: 25099239
-
Toward Trauma-Informed Pedagogy: An Intersectional Analysis of Pimping in Medical Education.Acad Med. 2022 Sep 1;97(9):1295-1298. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000004724. Epub 2022 May 3. Acad Med. 2022. PMID: 35507457
-
How shifting visual perspective during autobiographical memory retrieval influences emotion: A change in retrieval orientation.Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 Sep 26;16:928583. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.928583. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36226260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hippocampal network oscillations as mediators of behavioural metaplasticity: Insights from emotional learning.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018 Oct;154:37-53. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2018.02.022. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018. PMID: 29476822 Review.
Cited by
-
The Use of Retrieval Practice in the Health Professions: A State-of-the-Art Review.Behav Sci (Basel). 2025 Jul 17;15(7):974. doi: 10.3390/bs15070974. Behav Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723757 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- The art of pimping. Brancati FL. JAMA. 1989;262:89–90. - PubMed
-
- Prefrontal cortex and long-term memory encoding: an integrative review of findings from neuropsychology and neuroimaging. Blumenfeld RS, Ranganath C. Neuroscientist. 2007;13:280–291. - PubMed
-
- Blumenfeld H. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates Inc. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates Inc.; 2021. Neuroanatomy Through Clinical Cases 3rd Edition.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
