Corneal Deposits Following Combined Gatifloxacin and Prednisolone Therapy Post-Keratoplasty: A Report of a Rare Case
- PMID: 39131012
- PMCID: PMC11315940
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.64283
Corneal Deposits Following Combined Gatifloxacin and Prednisolone Therapy Post-Keratoplasty: A Report of a Rare Case
Abstract
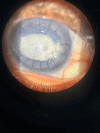
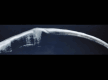
Corneal deposits associated with topical medications, particularly fluoroquinolones, are a recognized complication in ophthalmic practice. We present a case of a 66-year-old female with pseudophakic bullous keratopathy who developed corneal crystalline deposits following prolonged use of gatifloxacin and prednisolone eye drops post-penetrating keratoplasty. The patient presented with diminished vision and significant corneal opacity in the affected eye. Anterior segment examination and OCT imaging confirmed deposits extending from the epithelium to the anterior stroma. Management included corneal scrapping and transition to topical tobramycin and propylene glycol eye drops, resulting in the resolution of deposits and improvement in vision. This case underscores the importance of vigilant monitoring and judicious use of topical medications to mitigate adverse effects in high-risk ophthalmic patients undergoing corneal procedures.
Keywords: corneal deposit; corneal scrapping; gatifloxacin; keratoplasty; prednisolone.
Copyright © 2024, Modgil et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


References
-
- Moxifloxacin induced keratopathy. Janti SS, Shinisha DP, Sudhakar KS. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijceo.2021.116 Indian J Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2021;7:594–595.
-
- Ocular toxicity of fluoroquinolones. Thompson AM. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-9071.2007.01552.x. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007;35:566–577. - PubMed
-
- Corneal intrastromal gatifloxacin crystal deposits after penetrating keratoplasty. Awwad ST, Haddad W, Wang MX, Parmar D, Conger D, Cavanagh HD. Eye Contact Lens. 2004;30:169–172. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
