In silico evaluation of potential breast cancer receptor antagonists from GC-MS and HPLC identified compounds in Pleurotus ostreatus extracts
- PMID: 39131188
- PMCID: PMC11310660
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra03832k
In silico evaluation of potential breast cancer receptor antagonists from GC-MS and HPLC identified compounds in Pleurotus ostreatus extracts
Abstract
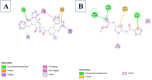
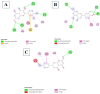
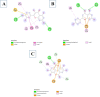
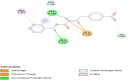
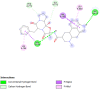
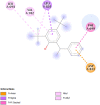
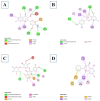
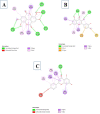
Introduction: Pharmacotherapeutic targets for breast cancer include the estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and human epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Inhibitors of these receptors could be interesting therapeutic candidates for the treatment and management of breast cancer (BC). Aim: This study used GC-MS and HPLC to identify bioactive compounds in Pleurotus ostreatus (P. ostreatus) extracts and applied in silico methods to identify potent EGFR, ER, and PR inhibitors from the compounds as potential drug candidates. Method: GC-MS and HPLC were used to identify bioactive chemicals in P. ostreatus extracts of aqueous (PO-A), methanol (PO-M), ethanol (PO-E), chloroform (PO-C), and n-hexane (PO-H). The ER, PR, and EGFR model optimization and molecular docking of compounds/control inhibitors in the binding pocket were simulated using AutoDock Vina in PyRx. The drug-likeness, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic features of prospective docking leads were all anticipated. Result: The results indicated the existence of 29 compounds in PO-A, 36 compounds in PO-M and PO-E, 42 compounds in PO-C, and 22 compounds in PO-H extracts. With ER, only o-tolylamino-acetic acid (4-nitro-benzylidene)-hydrazide (-7.5 kcal mol-1) from the ethanolic extract could bind to the receptor. PR and EGFR, on the other hand, identified several compounds with higher binding affinities than the control. Ergotaman-3',6',18-trione (-8.1 kcal mol-1), 5,10-diethoxy-2,3,7,8-tetrahydro-1H,6H-dipyrrolo[1,2-a:1',2'-d]pyrazine (-7.8 kcal mol-1) from the aqueous extract; o-tolylamino-acetic acid (4-nitro-benzylidene)-hydrazide (-8.4 kcal mol-1) from the ethanolic extract had better binding affinity compared to progesterone (-7.7 kcal mol-1). Likewise, ergotaman-3',6',18-trione (-9.7 kcal mol-1) from the aqueous extract and phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethyl ethyl) (-8.2 kcal mol-1) from the chloroform extract had better binding affinities compared to the control, gefitinib (-7.9 kcal mol-1) with regards to EGFR. None of the PO-H or PO-M extracts outperformed the control for any of the proteins. Phenols and flavonoids such as quercetin, luteolin, rutin, chrysin, apigenin, ellagic acid, and naringenin had better binding affinity to PR and EGFR compared to their control. Conclusion: The identified compounds in the class of phenols and flavonoids were better lead molecules due to their ability to strongly bind to the proteins' receptors. These compounds showed promising drug-like properties; they could be safe and new leads for creating anticancer medicines.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular Docking Appraisal of Pleurotus ostreatus Phytochemicals as Potential Inhibitors of PI3K/Akt Pathway for Breast Cancer Treatment.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2025 Feb 3;19:11779322251316864. doi: 10.1177/11779322251316864. eCollection 2025. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2025. PMID: 39906062 Free PMC article.
-
Elemental Analysis, Phytochemical Screening and Evaluation of Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Anticancer Activity of Pleurotus ostreatus through In Vitro and In Silico Approaches.Metabolites. 2022 Aug 31;12(9):821. doi: 10.3390/metabo12090821. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36144225 Free PMC article.
-
In-vitro Antioxidant, In-vitro and In-silico Ovarian Anticancer Activity (Ovarian Cancer Cells-PA1) and Phytochemical Analysis of Cissus quadrangularis L. Ethanolic Extract.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(10):1504-1512. doi: 10.2174/0113862073255558230926114444. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 37818574
-
Natural Phytocompounds from Common Indian Spices for Identification of Three Potential Inhibitors of Breast Cancer: A Molecular Modelling Approach.Molecules. 2022 Oct 5;27(19):6590. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196590. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36235128 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and Cytotoxicity of Extracts and Isolated Compounds from Artemisia abyssinica: A Combined Experimental and Computational Study.ACS Omega. 2024 Jul 10;9(29):31508-31520. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c01096. eCollection 2024 Jul 23. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39072116 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic Insights into the Anticancer Potential of Methoxyflavones Analogs: A Review.Molecules. 2025 Jan 16;30(2):346. doi: 10.3390/molecules30020346. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39860214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Docking Appraisal of Pleurotus ostreatus Phytochemicals as Potential Inhibitors of PI3K/Akt Pathway for Breast Cancer Treatment.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2025 Feb 3;19:11779322251316864. doi: 10.1177/11779322251316864. eCollection 2025. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2025. PMID: 39906062 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

