This is a preprint.
Saturation transposon mutagenesis enables genome-wide identification of genes required for growth and fluconazole resistance in the human fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans
- PMID: 39131341
- PMCID: PMC11312461
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.07.28.605507
Saturation transposon mutagenesis enables genome-wide identification of genes required for growth and fluconazole resistance in the human fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans
Update in
-
Landscape of essential growth and fluconazole-resistance genes in the human fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans.PLoS Biol. 2025 May 22;23(5):e3003184. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3003184. eCollection 2025 May. PLoS Biol. 2025. PMID: 40402997 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Fungi can cause devastating invasive infections, typically in immunocompromised patients. Treatment is complicated both by the evolutionary similarity between humans and fungi and by the frequent emergence of drug resistance. Studies in fungal pathogens have long been slowed by a lack of high-throughput tools and community resources that are common in model organisms. Here we demonstrate a high-throughput transposon mutagenesis and sequencing (TN-seq) system in Cryptococcus neoformans that enables genome-wide determination of gene essentiality. We employed a random forest machine learning approach to classify the Cryptococcus neoformans genome as essential or nonessential, predicting 1,465 essential genes, including 302 that lack human orthologs. These genes are ideal targets for new antifungal drug development. TN-seq also enables genome-wide measurement of the fitness contribution of genes to phenotypes of interest. As proof of principle, we demonstrate the genome-wide contribution of genes to growth in fluconazole, a clinically used antifungal. We show a novel role for the well-studied RIM101 pathway in fluconazole susceptibility. We also show that 5' insertions of transposons can drive sensitization of essential genes, enabling screenlike assays of both essential and nonessential components of the genome. Using this approach, we demonstrate a role for mitochondrial function in fluconazole sensitivity, such that tuning down many essential mitochondrial genes via 5' insertions can drive resistance to fluconazole. Our assay system will be valuable in future studies of C. neoformans, particularly in examining the consequences of genotypic diversity.
Figures
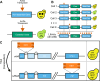

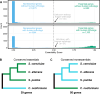


References
-
- Denning DW. Global incidence and mortality of severe fungal disease. Lancet Infect Dis [Internet]. 2024. Jan 12 [cited 2024 Feb 8];0(0). Available from: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(23)00692... - PubMed
-
- Perfect JR. Cryptococcus neoformans: A sugar-coated killer with designer genes. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2005;45(3):395–404. - PubMed
-
- Hagen F, Khayhan K, Theelen B, Kolecka A, Polacheck I, Sionov E, et al. Recognition of seven species in the Cryptococcus gattii/Cryptococcus neoformans species complex. Fungal Genet Biol. 2015. May 1;78:16–48. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
