Prognosis of PCI in the Older Adult Population: Outcomes From the Multicenter Prospective e-ULTIMASTER Registry
- PMID: 39131453
- PMCID: PMC11308062
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jscai.2022.100442
Prognosis of PCI in the Older Adult Population: Outcomes From the Multicenter Prospective e-ULTIMASTER Registry
Abstract
Background: Older adult patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) are usually excluded from clinical trials. This study aimed to assess 1-year clinical outcomes in patients aged >80 years.
Methods: This all-comer registry included patients who underwent PCI using the Ultimaster stent. Primary clinical endpoint was target lesion failure (TLF), a composite of cardiac death (CD), target vessel-related myocardial infarction (TV-MI), or clinically indicated target lesion revascularization (CD-TLR).
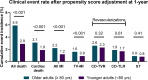
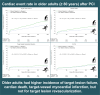
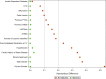
Results: In total, 3286 (8.8%) patients aged ≥80 years were compared with 33,912 patients aged <80 years. The older adult patients included more women, had more comorbidities and exhibited more complex coronary anatomy. The incidence of TLF was higher in the older adult group (5.6% vs 3.0%, P < .0001), as well as for all-cause mortality (6.2% vs 1.7%, P < .0001), CD (3.3% vs 1.1%, P < .0001), and TV-MI (1.7% vs 0.8%, P < .0001), but not for CD-TLR (1.9% vs 1.7%, P = .15). After the inverse propensity score weighted analysis, aged ≥80 years was associated with increased risk of TLF (HR, 1.42; 95% CI, 1.22-1.66; P < .0001), CD (HR, 1.67; 95% CI, 1.136-2.06; P < .0001), and TV-MI (HR, 1.66; 95% CI, 1.24-2.24; P < .001) but not for CD-TLR (HR, 1.10; 95% CI, 0.85-1.43; P = .45).
Conclusion: Older adult patients had a higher incidence of TLF, CD, and TV-MI but with no difference in the incidence of recurrent revascularization or stent thrombosis. Although PCI in older adults is relatively safe, higher rates of cardiac events should be considered.
Keywords: age; coronary artery disease; elderly; older adults; outcome; stent; vascular disease.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Tsounis D., Deftereos S., Bouras G., et al. High sensitivity troponin in cardiovascular disease. Is there more than a marker of myocardial death? Curr Top Med Chem. 2013;13(2):201–215. - PubMed
-
- Renilla A., Barreiro M., Barriales V., Torres F., Alvarez P., Lambert J.L. Management and risk factors for mortality in very elderly patients with acute myocardial infarction. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2013;13(1):146–151. - PubMed
-
- Trucil D.E., Lundebjerg N.E., Busso D.S. RESEARCH When it comes to older adults, language matters and is changing: American Geriatrics Society update on reframing aging style changes. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021;69(1):265–267. - PubMed
-
- Sawant A.C., Josey K., Plomondon M.E., et al. Temporal trends, complications, and predictors of outcomes among nonagenarians undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: insights from the Veterans Affairs Clinical Assessment, Reporting, and Tracking Program. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017;10(13):1295–1303. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

