Association of serum 25-hydroxyvitamins D2 and D3 with hearing loss in US adults: analysis from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2015-2016
- PMID: 39131738
- PMCID: PMC11310169
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1390953
Association of serum 25-hydroxyvitamins D2 and D3 with hearing loss in US adults: analysis from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2015-2016
Abstract
Background: Hearing loss (HL) is increasingly recognized as a significant global public health issue, and research on its relationship with vitamin D levels has gained wider attention. However, the association between serum biomarkers 25-hydroxyvitamin D2 (25(OH)D2) and D3 (25(OH)D3) with different types of HL remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate the potential association of serum 25(OH)D2 and 25(OH)D3 with HL in US adults.
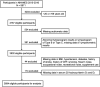
Methods: A sample of 3,684 individuals aged 20-69 years from the 2015-2016 National Health and Nutrition Examination (NHANES) was analyzed in this study. HL was defined as a pure tone average > 25 dB in either ear at low frequencies (500, 1,000, 2000 Hz), speech frequencies (500, 1,000, 2000, 4,000 Hz), and high frequencies (3,000, 4,000, 6,000, 8,000 Hz). Logistic regression was employed to examine the association between serum 25(OH)D2 and 25(OH)D3 and HL. The study population was then stratified by age, gender, race, and education level to analyze potential differences between adults in different subgroups.
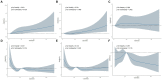
Results: In the multivariate analysis, it was found that serum 25(OH)D2 was independently associated with low-frequency hearing loss (LFHL) (OR: 1.012 [95% CI, 1.005-1.020]) and speech-frequency hearing loss (SFHL) (OR: 1.011 [95% CI, 1.003-1.018]). Restrictive cubic spline analysis demonstrated a linear dose-response relationship between serum 25(OH)D2 levels and LFHL (p for linearity <0.001), as well as SFHL (p for linearity = 0.001). Conversely, an L-shaped association was observed between serum 25(OH)D3 levels and both LFHL (p for nonlinearity = 0.014) and SFHL (p for nonlinearity = 0.025), with threshold values identified at 35.3 and 36.5 nmol/L, respectively. Higher levels of serum 25(OH)D3 were associated with a lower probability of high-frequency hearing loss (HFHL) (OR: 0.994 [95% CI, 0.989-0.999]), with a threshold value identified at 53.9 nmol/L. Furthermore, a significant interaction between diabetes and serum 25(OH)D2 in LFHL was revealed through subgroup analysis (p = 0.041). In the non-diabetic population, serum 25(OH)D2 maintained its association with LFHL.
Conclusion: Our findings suggested a positive association between serum 25(OH)D2 concentrations and both LFHL and SFHL in the studied cohort. Additionally, an L-shaped relationship was found between serum 25(OH)D3 and LFHL and SFHL, and higher levels of serum 25(OH)D3 were identified to be associated with a lower risk of HFHL.
Keywords: 25-hydroxyvitamin D2; 25-hydroxyvitamin D3; L-shaped association; dose–response; hearing loss.
Copyright © 2024 Chen, Gao, Wang, Pan, Chen, Sheng, Chen and Ye.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between caffeine intake from foods and beverages in the diet and hearing loss in United States adults.Front Neurol. 2024 Jul 24;15:1436238. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1436238. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39114534 Free PMC article.
-
L-shaped relationship between dietary niacin intake and hearing loss in United States adults: National health and nutrition examination survey.PLoS One. 2025 Feb 25;20(2):e0319386. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319386. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39999158 Free PMC article.
-
L-shaped relationship between dietary magnesium intake and hearing loss in US adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.Int J Audiol. 2025 May 26:1-10. doi: 10.1080/14992027.2025.2505548. Online ahead of print. Int J Audiol. 2025. PMID: 40418757
-
L-Shaped Associations Between Composite Dietary Antioxidant Index and Hearing Loss: A Cross-Sectional Study From the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.Biol Res Nurs. 2025 Jan;27(1):28-36. doi: 10.1177/10998004241261400. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Biol Res Nurs. 2025. PMID: 38869482
-
The Inverted-U Relationship Between Dietary Inflammatory Potential and Hearing Loss Among Adults Aged 20 Years and Over in the United States: A Cross-Sectional Study.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Dec 8;14:6671-6683. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S337737. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34916819 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association between hepatitis A B vaccination and hearing loss across frequencies based on NHANES.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23360. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07168-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40603463 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the causal link between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations and idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Insights gained from a Mendelian randomization study involving two independent samples.PLoS One. 2025 May 19;20(5):e0322898. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322898. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40388403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Deafness and hearing loss. (2020). Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss
-
- World Health Organization . Addressing the rising prevalence of hearing Loss. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2018).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

