Assessing the Anxiolytic and Relaxation Effects of Cinnamomum camphora Essential Oil in University Students: A Comparative Study of EEG, Physiological Measures, and Psychological Responses
- PMID: 39131857
- PMCID: PMC11312375
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1423870
Assessing the Anxiolytic and Relaxation Effects of Cinnamomum camphora Essential Oil in University Students: A Comparative Study of EEG, Physiological Measures, and Psychological Responses
Abstract
Background: Cinnamomum camphora is a commercially important tree species in China, and it's also a common native tree in the forests of southern China. However, literature on the impact of Cinnamomum camphora essential oil (CCEO) on human psychophysiological activity is scarce. Hence, the primary objective of this study was to examine the effect of exposure to CCEO on the functioning of the human autonomic nervous system, electroencephalographic (EEG) activity, and emotional state.
Methods: Forty-three healthy university students participated. The data collected included heart rate (HR), blood pressure (BP), pulse rate, blood oxygen saturation (SpO2), electroencephalographic (EEG) activity, and the results of the Profile of Mood States (POMS) test.
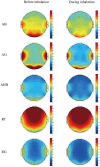
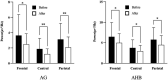
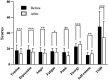
Results: A drop in diastolic pressure (DBP) and pulse rate was also noticed after participants inhaled CCEO. Furthermore, EEG studies have demonstrated notable reductions in absolute beta (AB), absolute gamma (AG), absolute high beta (AHB), and relative gamma (RG) power spectra during exposure to CCEO. Conversely, the relative theta (RT) and power spectra values showed a significant increase. Additionally, the finding from POMS indicated that the fragrance evoked positive emotions and suppressed negative feelings.
Conclusion: The results suggest that exposure to CCEO may promote mental and physical relaxation, facilitate cognitive processes such as memory and attention, and enhance mood states.
Keywords: Cinnamomum camphora; aromatherapy; electroencephalogram; essential oil; natural therapy.
Copyright © 2024 Gong, Yang, Xu, Yao, Lin and Chang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Beili Z. (1995). Brief introduction of POMS scale and its model for China. J. Tianjin Inst. Phys. Educ. 1, 35–37.
-
- Choi N., Yamanaka T., Takemura A., Kobayashi T., Eto A., Hirano M. (2022). Impact of indoor aroma on students’ mood and learning performance. Build. Environ. 223:109490. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.109490 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

