An Acoustofluidic Picoinjector
- PMID: 39131888
- PMCID: PMC11308560
- DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2024.136294
An Acoustofluidic Picoinjector
Abstract
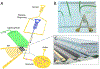
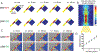
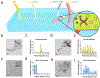
Droplet microfluidics has emerged as a valuable technology for a multitude of chemical and biomedical applications, offering the capability to create independent microenvironments for high-throughput assays. Central to numerous droplet microfluidic applications is the picoinjection of materials into individual droplets, yet existing picoinjection methods often exhibit high power requirements, lack biocompatibility, and/or suffer from limited controllability. Here, we present an acoustofluidic picoinjector that generates acoustic pressure at the droplet interface to enable on-demand, energy-efficient, and biocompatible injection at high precision. We validate our platform by performing acid-base titrations by iteratively injecting picoliter volume reagents into droplets to induce pH transitions detectable by color change in solution. Additionally, we demonstrate the versatility of the acoustofluidic picoinjector in the synthesis of metallic nanoparticles, yielding highly monodisperse and reproducible particle morphologies compared to conventional bulk-phase techniques. By facilitating controlled delivery of reagents or biological samples with unparalleled accuracy, acoustofluidic picoinjection broadens the utility of droplet microfluidics for a myriad of applications in chemical and biological research.
Keywords: Acoustofluidics; droplet microfluidics; nanoparticle synthesis; picoinjection.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest T.J.H. has co-founded a startup company, Ascent Bio-Nano Technologies Inc., to commercialize technologies involving acoustofluidics and acoustic tweezers. The authors declare no other competing interests.
Figures
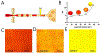
References
-
- Teh S-Y, Lin R, Hung L-H, Lee AP, Droplet microfluidics. Lab on a Chip 8, 198–220 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Shang L, Cheng Y, Zhao Y, Emerging droplet microfluidics. Chemical reviews 117, 7964–8040 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Abdelgawad M, Wheeler AR, The digital revolution: a new paradigm for microfluidics. Advanced Materials 21, 920–925 (2009).
-
- Zhang H, Guzman AR, Wippold JA, Li Y, Dai J, Huang C, Han A, An ultra high-efficiency droplet microfluidics platform using automatically synchronized droplet pairing and merging. Lab on a Chip 20, 3948–3959 (2020). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

