Nrf2-Mediated Antioxidant Response and Drug Efflux Transporters Upregulation as Possible Mechanisms of Resistance in Photodynamic Therapy of Cancers
- PMID: 39131905
- PMCID: PMC11313505
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S457749
Nrf2-Mediated Antioxidant Response and Drug Efflux Transporters Upregulation as Possible Mechanisms of Resistance in Photodynamic Therapy of Cancers
Abstract
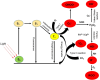
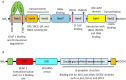
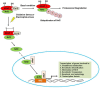
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a groundbreaking approach involving the induction of cytotoxic reactive oxygen species (ROS) within tumors through visible light activation of photosensitizers (PS) in the presence of molecular oxygen. This innovative therapy has demonstrated success in treating various cancers. While PDT proves highly effective in most solid tumors, there are indications that certain cancers exhibit resistance, and some initially responsive cancers may develop intrinsic or acquired resistance to PDT. The molecular mechanisms underlying this resistance are not fully understood. Recent evidence suggests that, akin to other traditional cancer treatments, the activation of survival pathways, such as the KEAP1/Nrf2 signaling pathway, is emerging as an important mechanism of post-PDT resistance in many cancers. This article explores the dual role of Nrf2, highlighting evidence linking aberrant Nrf2 expression to treatment resistance across a range of cancers. Additionally, it delves into the specific role of Nrf2 in the context of photodynamic therapy for cancers, emphasizing evidence that suggests Nrf2-mediated upregulation of antioxidant responses and induction of drug efflux transporters are potential mechanisms of resistance to PDT in diverse cancer types. Therefore, understanding the specific role(s) of Nrf2 in PDT resistance may pave the way for the development of more effective cancer treatments using PDT.
Keywords: Nrf2; antioxidant response; oxidative stress; photodynamic therapy; tumor resistance.
© 2024 Ajuwon et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global health estimates 2016: disease burden by cause, age, sex, by country and by region, 2000–2016. World Health Organization. 2018; Geneva. Available from: https://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/estimates/en/index1.... Accessed August 30, 2021.
-
- Kraybill WG, Harris J, Spiro IJ, et al. Long-term results of a Phase 2 study of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy in the management of high-risk, high-grade, soft tissue sarcomas of the extremities and body wall: radiation therapy oncology group trial 9514. Cancer. 2010;116(19):4613–4621. doi:10.1002/cncr.25350 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

