Role of myocardial microRNAs in the long-term ventricular remodelling of patients with aortic stenosis
- PMID: 39131907
- PMCID: PMC11311707
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjopen/oeae060
Role of myocardial microRNAs in the long-term ventricular remodelling of patients with aortic stenosis
Abstract
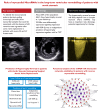
Aims: We hypothesize that miRs are key players in the dynamics of the hypertrophy phenotype in aortic stenosis (AS) patients. In our study, we aimed to identify the transcriptional patterns (protein-coding transcripts and miRs) from myocardial sample biopsies that could be associated with the absence of left ventricular (LV) mass regression after aortic valve replacement (AVR) in patients with severe AS and LV hypertrophy.
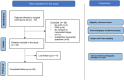
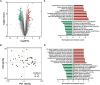
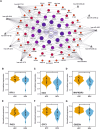
Methods and results: We prospectively included 40 patients with severe AS, LV hypertrophy, and preserved ejection fraction undergoing AVR. Myocardial biopsies obtained during surgery were analysed for transcriptomic analysis performed by next-generation sequencing. At a 1-year follow-up, no hypertrophy reversal was observed in about half of the patients in the absence of patient-prosthesis mismatch and prosthesis dysfunction of uncontrolled hypertension. Predictors of mass regression were assessed from clinical, echocardiographic, and biochemical variables as well as from 300 miRs obtained from myocardial specimens, allowing the identification 29 differentially expressed. miR-4709-3p was found as a positive independent predictor of hypertrophy regression together with high-sensitivity troponin T (cTNT-hs) as a negative predictor. Gene transcripts RFX1, SIX5, MAPK8IF3, and PKD1 were predicted as simultaneous targets of five upregulated miRs suggesting its importance in LV hypertrophy.
Conclusion: In our cohort, tissue miR-4709-3p and cTNT-hs were independent predictors of hypertrophy regression. The hypertrophy reversal process will likely depend from a complex network where miRNAs may have an important role, allowing a potential opportunity for therapy.
Keywords: Aortic stenosis; Cardiac remodelling; MicroRNA; Prognosis.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: none declared.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

