Inflammatory Trajectory and Anti-Inflammatory Pharmacotherapy in Frozen Elephant Trunk-Treated Acute Type I Aortic Dissection
- PMID: 39132007
- PMCID: PMC11307765
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jscai.2024.101935
Inflammatory Trajectory and Anti-Inflammatory Pharmacotherapy in Frozen Elephant Trunk-Treated Acute Type I Aortic Dissection
Abstract
Background: Acute DeBakey type I aortic dissection is associated with high morbidity and mortality. Little is known regarding the role of leukocyte trajectory in prognosis.
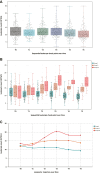
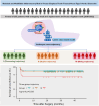
Methods: We included adult acute DeBakey type I aortic dissection patients with emergency frozen elephant trunk and total arch replacement in 2 cardiovascular centers (2020-2022). We used latent class mixed model to group patients according to their leukocyte patterns from hospital admission to the first 5 days after surgery. We investigated the association of leukocyte trajectory and 30-day and latest follow-up mortality (October 31, 2023), exploratorily analyzing the effects of ulinastatin treatment on outcome.
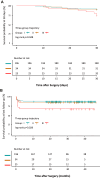
Results: Of 255 patients included, 3 distinct leukocyte trajectories were identified: 196 in group I (decreasing trajectory), 34 in group II (stable trajectory), and 25 in group III (rising trajectory). Overall, 30-day mortality was 25 (9.8%), ranging from 8.2% (16/196) in group I, 8.8% (3/34) in group II, to 24.0% (6/25) in group III (P for trend = .036). Group III was associated with higher mortality both at 30 days (adjusted hazard ratio, 3.260; 95% CI, 1.071-9.919; P = .037) and at the last follow-up (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.840; 95% CI, 1.098-7.345; P = .031) compared with group I.
Conclusions: Distinct and clinically relevant groups can be identified by analyzing leukocyte trajectories, and a rising trajectory was associated with higher short-term and midterm mortality.
Keywords: inflammatory; latent class extend mixed model; leukocyte trajectory; type I aortic dissection.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic implication of residual inflammatory trajectories in acute type I aortic dissection: dual-center prospective cohort study.Int J Surg. 2024 Jun 1;110(6):3346-3356. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001245. Int J Surg. 2024. PMID: 38445499 Free PMC article.
-
Frozen elephant trunk does not increase incidence of paraplegia in patients with acute type A aortic dissection.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020 Apr;159(4):1189-1196.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2019.03.097. Epub 2019 Apr 14. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 31126657
-
Fate of distal aorta after frozen elephant trunk and total arch replacement for type A aortic dissection in Marfan syndrome.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019 Mar;157(3):835-849. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.07.096. Epub 2018 Aug 24. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019. PMID: 30635189
-
A Meta-Analysis of Total Arch Replacement With Frozen Elephant Trunk in Acute Type A Aortic Dissection.Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2016 Jan;50(1):33-46. doi: 10.1177/1538574415624767. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2016. PMID: 26767803 Review.
-
The frozen elephant trunk technique in acute DeBakey type I aortic dissection.Turk Gogus Kalp Damar Cerrahisi Derg. 2020 Jul 28;28(3):411-418. doi: 10.5606/tgkdc.dergisi.2020.20462. eCollection 2020 Jul. Turk Gogus Kalp Damar Cerrahisi Derg. 2020. PMID: 32953202 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of thymosin α1 on Immune response and organ function in acute aortic dissection surgery: PANDA II trial protocol.Future Cardiol. 2025 Jun;21(7):447-454. doi: 10.1080/14796678.2025.2505401. Epub 2025 May 14. Future Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40367062 Clinical Trial.
-
Protective effect of ulinastatin against negative inflammatory response and organ dysfunction in acute aortic dissection surgery: The PANDA trial.Cell Rep Med. 2025 Jan 21;6(1):101888. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101888. Cell Rep Med. 2025. PMID: 39842406 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Liu H., Qian S.C., Zhang Y.Y., et al. A novel inflammation-based risk score predicts mortality in acute Type A aortic dissection surgery: the additive anti-inflammatory action for aortopathy and arteriopathy score. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2022;6(6):497–510. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2022.08.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu H., Qian S.C., Shao Y.F., Li H.Y. Additive Anti-inflammatory Action for Aortopathy & Arteriopathy (5A) Investigators Group. Anti-inflammatory effect of ulinastatin on the association between inflammatory phenotypes in acute type A aortic dissection. J Inflam Res. 2022;15:3709–3718. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S369703. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

