A review of evaluation approaches for explainable AI with applications in cardiology
- PMID: 39132011
- PMCID: PMC11315784
- DOI: 10.1007/s10462-024-10852-w
A review of evaluation approaches for explainable AI with applications in cardiology
Abstract
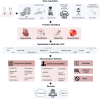
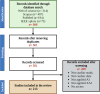
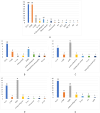
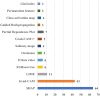
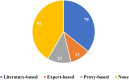
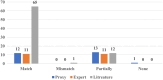
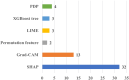
Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) elucidates the decision-making process of complex AI models and is important in building trust in model predictions. XAI explanations themselves require evaluation as to accuracy and reasonableness and in the context of use of the underlying AI model. This review details the evaluation of XAI in cardiac AI applications and has found that, of the studies examined, 37% evaluated XAI quality using literature results, 11% used clinicians as domain-experts, 11% used proxies or statistical analysis, with the remaining 43% not assessing the XAI used at all. We aim to inspire additional studies within healthcare, urging researchers not only to apply XAI methods but to systematically assess the resulting explanations, as a step towards developing trustworthy and safe models.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s10462-024-10852-w.
Keywords: AI; Cardiac; Evaluation; XAI.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no Conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
How Explainable Artificial Intelligence Can Increase or Decrease Clinicians' Trust in AI Applications in Health Care: Systematic Review.JMIR AI. 2024 Oct 30;3:e53207. doi: 10.2196/53207. JMIR AI. 2024. PMID: 39476365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A literature review of artificial intelligence (AI) for medical image segmentation: from AI and explainable AI to trustworthy AI.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Dec 5;14(12):9620-9652. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-723. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 39698664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of Explainable Artificial Intelligence in Diagnosis and Surgery.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Jan 19;12(2):237. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12020237. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential properties and explanation effectiveness of explainable artificial intelligence in healthcare: A systematic review.Heliyon. 2023 May 8;9(5):e16110. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16110. eCollection 2023 May. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37234618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human-centered evaluation of explainable AI applications: a systematic review.Front Artif Intell. 2024 Oct 17;7:1456486. doi: 10.3389/frai.2024.1456486. eCollection 2024. Front Artif Intell. 2024. PMID: 39484154 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Large Language Models in Genomics-A Perspective on Personalized Medicine.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Apr 23;12(5):440. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12050440. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40428059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Explainable AI in early autism detection: a literature review of interpretable machine learning approaches.Discov Ment Health. 2025 Jul 1;5(1):98. doi: 10.1007/s44192-025-00232-3. Discov Ment Health. 2025. PMID: 40593180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in Bicuspid Aortic Valve Disease: A Review of the Existing Literature.Cureus. 2025 Jan 29;17(1):e78192. doi: 10.7759/cureus.78192. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40027070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Ischemic Heart Disease Prevention.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2025 Feb 1;27(1):44. doi: 10.1007/s11886-025-02203-0. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39891819 Review.
-
Explainable Artificial Intelligence in Radiological Cardiovascular Imaging-A Systematic Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 May 31;15(11):1399. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15111399. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40506971 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aas K, Jullum M, Løland A (2021) Explaining individual predictions when features are dependent: more accurate approximations to Shapley values. Artif Intell 298:103502
-
- Abdullah TA, Zahid MSBM, Tang TB, Ali W, Nasser M (2022) Explainable deep learning model for cardiac arrhythmia classification. In: 2022 International conference on future trends in smart communities (ICFTSC). IEEE, pp 87–92
-
- Abdullah TA, Zahid MSM, Ali W, Hassan SU (2023) B-LIME: an improvement of lime for interpretable deep learning classification of cardiac arrhythmia from ECG signals. Processes 11(2):595
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
