Combination of Proton Pump Inhibitors and Food Elimination Diet for Eosinophilic Esophagitis Refractory to Monotherapy
- PMID: 39132073
- PMCID: PMC11307866
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gastha.2022.04.002
Combination of Proton Pump Inhibitors and Food Elimination Diet for Eosinophilic Esophagitis Refractory to Monotherapy
Abstract
Background and aims: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an antigen-mediated inflammatory esophageal disease that is commonly treated with high-dose proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs), topical corticosteroids, or food elimination diet (FED) monotherapy. Combination treatment has not been well studied in the management of EoE. We aimed to determine if PPI and FED combination therapy was able to induce histologic remission in patients with EoE refractory to monotherapy.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study identifying patients with EoE that was refractory to PPI monotherapy and FED monotherapy but histologically responsive to PPI and FED combination therapy. We also identified symptom changes through chart review.
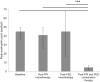
Results: Out of 405 EoE patients, 12 patients were identified with EoE that was refractory to PPI monotherapy and FED monotherapy but histologically responsive to PPI and FED combination therapy. Out of 12 patients, 11 (91.67%) noted resolution of symptoms while on combination therapy. Comparative analysis of peak eosinophil counts showed that patients achieved a median of 4.5 eos/hpf (interquartile range [IQR], 2-6.5), which was significantly decreased compared to baseline (median, 45; IQR, 35.5-50; Wilcoxon signed-rank test, P < .001), PPI monotherapy (median, 41; IQR, 26-50; Wilcoxon signed-rank test, P < .001), and FED monotherapy (median, 45; IQR, 17-67.5; Wilcoxon signed-rank test, P < .001).
Conclusion: Our work shows that patients with EoE refractory to PPI monotherapy and FED monotherapy can successfully achieve histologic remission and symptom benefit with PPI and FED combination therapy. Therefore, combination therapy should be considered a viable option for patients with EoE who fail treatment with first-line monotherapies.
Keywords: Eosinophils; FED; Histology; PPI.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures

References
-
- Laserna-Mendiata E.J., Casabona S., Savarino E., et al. Efficacy of therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis in real-world practice. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18:2903–2911. - PubMed
-
- Laserna-Mendiata E.J., Casabona S., Guagnozzi D., et al. Efficacy of proton pump inhibitor therapy for eosinophilic oesophagitis in 630 patients: results from the EoE connect registry. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020;52:798–807. - PubMed
-
- Navarro P., Laserna-Medieta E.J., Guagnozzi D., et al. Proton pump inhibitor therapy reverses endoscopic features of fibrosis in eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig Liver Dis. 2021;53:1479–1485. - PubMed
-
- Molina-Infante J., Arias A., Alcedo J., et al. Step-up empiric elimination diet for pediatric and adult eosinophilic esophagitis: the 2-4-6 study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141:1365–1372. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

