Development of semisynthetic saponin immunostimulants
- PMID: 39132259
- PMCID: PMC11315725
- DOI: 10.1007/s00044-024-03227-x
Development of semisynthetic saponin immunostimulants
Abstract
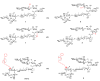
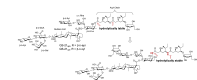
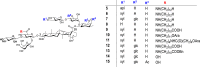
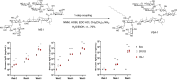
Many natural saponins demonstrate immunostimulatory adjuvant activities, but they also have some inherent drawbacks that limit their clinical use. To overcome these limitations, extensive structure-activity-relationship (SAR) studies have been conducted. The SAR studies of QS-21 and related saponins reveal that their respective fatty side chains are crucial for potentiating a strong cellular immune response. Replacing the hydrolytically unstable ester side chain in the C28 oligosaccharide domain with an amide side chain in the same domain or in the C3 branched trisaccharide domain is a viable approach for generating robust semisynthetic saponin immunostimulants. Given the striking resemblance of natural momordica saponins (MS) I and II to the deacylated Quillaja Saponaria (QS) saponins (e.g., QS-17, QS-18, and QS-21), incorporating an amide side chain into the more sustainable MS, instead of deacylated QS saponins, led to the discovery of MS-derived semisynthetic immunostimulatory adjuvants VSA-1 and VSA-2. This review focuses on the authors' previous work on SAR studies of QS and MS saponins.
Keywords: Immunostimulant; Momordica cochinchinensis; Saponin; VSA-1; VSA-2; Vaccine adjuvant.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): PW is an inventor on the patents and patent applications based on this work. The University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) has intellectual property rights to VSA adjuvants developed in PW’s laboratory. PW is a co-founder of Adjuvax LLC.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Structure-Activity Relationship Study of Momordica Saponin II Derivatives as Vaccine Adjuvants.J Med Chem. 2022 Nov 10;65(21):14589-14598. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01087. Epub 2022 Nov 1. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36318612 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Improved Vaccine Adjuvants Based on the Saponin Natural Product QS-21 through Chemical Synthesis.Acc Chem Res. 2016 Sep 20;49(9):1741-56. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00242. Epub 2016 Aug 28. Acc Chem Res. 2016. PMID: 27568877 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Effect on Adjuvanticity of Saponins.J Med Chem. 2020 Mar 26;63(6):3290-3297. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b02063. Epub 2020 Feb 26. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32101001 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of immunostimulatory saponins: A sweet challenge for carbohydrate chemists.Carbohydr Res. 2023 Aug;530:108851. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2023.108851. Epub 2023 May 23. Carbohydr Res. 2023. PMID: 37257206 Review.
-
Natural and Synthetic Saponins as Vaccine Adjuvants.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Mar 5;9(3):222. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9030222. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33807582 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing Thalassochemicals: Marine Saponins as Bioactive Agents in Nutraceuticals and Food Technologies.Mar Drugs. 2025 May 26;23(6):227. doi: 10.3390/md23060227. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40559636 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Garçon N, Leroux-Roels G, Cheng W-F. Vaccine Adjuvants. In: Garçon N, Stern PL, Cunningham AL, editors. Understanding Modern Vaccines Perspectives in Vaccinology 1. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2011. p. 89–113.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
