Clinical Relevance of Impaired Physiological Assessment After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A Meta-analysis
- PMID: 39132337
- PMCID: PMC11307483
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jscai.2022.100448
Clinical Relevance of Impaired Physiological Assessment After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A Meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Despite the optimal angiographic result of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), residual disease at the site of the culprit lesion can lead to major adverse cardiac events. Post-PCI physiological assessment can identify residual stenosis. This meta-analysis aims to investigate data of studies examining post-PCI physiological assessment in relation to long-term outcomes.
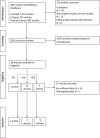
Methods: Studies were included in the meta-analysis after performing a systematic literature search on July 1, 2022. The primary end point was the incidence of major adverse cardiac events, vessel-orientated cardiac events, or target vessel failure.
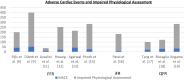
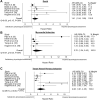
Results: Low post-PCI fractional flow reserve, reported in 7 studies with fractional flow reserve cutoff values between 0.84 and 0.90, including 4017 patients, was associated with an increased rate of the primary end point (hazard ratio [HR], 2.06; 95% CI, 1.37-3.08). One study reported about impaired post-PCI instantaneous wave-free ratio with instantaneous wave-free ratio cutoff value of 0.95 in relation to major adverse cardiac events, showing a significant association (HR, 3.38; 95% CI, 0.99-11.6; P = .04). Low post-PCI quantitative flow ratio, reported in 3 studies with quantitative flow ratio cutoff value between 0.89 and 0.91, including 1181 patients, was associated with an increased rate of vessel-orientated cardiac events (HR, 3.01; 95% CI, 2.10-4.32). Combining data of all modalities, impaired physiological assessment showed an increased rate of the primary end point (HR, 2.32; 95% CI, 1.71-3.16) and secondary end points, including death (HR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.04-1.89), myocardial infarction (HR, 2.70; 95% CI, 1.34-5.42) and target vessel revascularization (HR, 2.88; 95% CI, 1.91-4.35).
Conclusions: Impaired post-PCI physiological assessment is associated with increased adverse cardiac events and individual end points, including death, myocardial infarction, and target vessel revascularization. Therefore, prospective studies are awaited on whether physiology-based optimization of PCI results in better clinical outcomes.
Keywords: fractional flow reserve; instantaneous wave-free ratio; major adverse cardiac events; percutaneous coronary intervention; physiological assessment; quantitative flow ratio.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Figures




References
-
- Pijls N.H., De Bruyne B., Peels K., et al. Measurement of fractional flow reserve to assess the functional severity of coronary-artery stenoses. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(26):1703–1708. - PubMed
-
- Lee J.M., Choi K.H., Park J., et al. Physiological and clinical assessment of resting physiological indexes. Circulation. 2019;139(7):889–900. - PubMed
-
- Tonino P.A.L., De Bruyne B., Pijls N.H., et al. Fractional flow reserve versus angiography for guiding percutaneous coronary intervention. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(3):213–224. - PubMed
-
- Valgimigli M., Tebaldi M., Borghesi M., et al. Two-year outcomes after first- or second-generation drug-eluting or bare-metal stent implantation in all-comer patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: a pre-specified analysis from the PRODIGY study (PROlonging Dual antiplatelet Treatment After Grading stent-induced Intimal hyperplasia studY) JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;7(1):20–28. - PubMed
-
- Stone G.W., Maehara A., Lansky A.J., et al. A prospective natural-history study of coronary atherosclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(3):226–235. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

