Corticosteroid Therapy and Vascular Complications in Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: A Meta-analysis With Meta-regression
- PMID: 39132379
- PMCID: PMC11307401
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jscai.2022.100446
Corticosteroid Therapy and Vascular Complications in Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: A Meta-analysis With Meta-regression
Abstract
Background: Corticosteroid use is associated with vascular fragility, prolonged wound healing, and infections. Therefore, we sought to compare outcomes between patients with aortic stenosis undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement who were using corticosteroids versus those who were not.
Methods: This is a study-level meta-analysis and meta-regression of observational studies. The primary end points of this study were rates of vascular complication (both major and minor), life-threatening bleeding, and 30-day mortality. Secondary end points included acute kidney injury rates, annular rupture, cardiac tamponade, closure device failure, coronary obstruction, periprocedural myocardial infarction, permanent pacemaker implantation, stroke, and specific vascular complications with its complementary therapy.
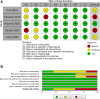
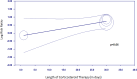
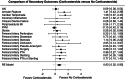
Results: Across the studies, patients were slightly predominantly female, older, and had a mean left ventricular ejection fraction of more than 50% with an intermediate Logistic EuroScore II. Significant differences were observed in the vascular complication rates between patients on corticosteroids and those who were corticosteroid-free (relative risk, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.35-0.90; P <.001), driven primarily by arterial occlusion, surgery, balloon angioplasty, and stenting (relative risk, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.32-0.93; P <.05). There was no difference in the 30-day mortality. No differences were seen in the length of corticosteroid therapies. For the secondary outcomes, there was an increased risk of annular rupture and cardiac tamponade in patients taking corticosteroids.
Conclusions: In conclusion, this is the first meta-analysis with meta-regression that showed a higher risk for vascular complications and life-threatening bleeding in patients on corticosteroid therapy undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement, despite no increase in the risk of 30-day mortality.
Keywords: corticosteroids; heart valve prosthesis implantation; meta-analysis; mortality; transcatheter aortic valve replacement; vascular complications.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Figures



References
-
- Mack M.J., Leon M.B., Thourani V.H., et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement with a balloon-expandable valve in low-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(18):1695–1705. - PubMed
-
- Popma J.J., Deeb G.M., Yakubov S.J., et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement with a self-expanding valve in low-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(18):1706–1715. - PubMed
-
- Ellis S.G., Semenec T., Lander K., Franco I., Raymond R., Whitlow P.L. Effects of long-term prednisone (> or =5 mg) use on outcomes and complications of percutaneous coronary intervention. Am J Cardiol. 2004;93(11):1389–1390. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

