Trimethylamine N-oxide promotes the proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cell through the MAPK pathway
- PMID: 39133354
- PMCID: PMC11319703
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-01178-8
Trimethylamine N-oxide promotes the proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cell through the MAPK pathway
Abstract
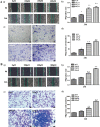
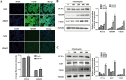
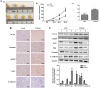
Trimethylamine-n-oxide (TMAO) is a metabolite of intestinal flora following the consumption of phosphatidylcholine-rich foods. Clinical cohort studies have shown that plasma TMAO may be a risk factor for cancer development, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but fundamental research data supporting this hypothesis are lacking. In this study, HCC cells were treated with TMAO in vivo and in vitro to evaluate the effect on some indicators related to the malignancy degree of HCC, and the relevant molecular mechanisms were explored. In vitro, TMAO promoted the proliferation and migration of HCC cells and significantly upregulated the expression of proteins related to epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT). In vivo, after HCC cells were inoculated subcutaneously in nude mice given water containing TMAO, the tumors grew faster and larger than those in the mice given ordinary water. The immunohistochemistry analysis showed that proliferation, migration and EMT-related proteins in the tumor tissues were significantly upregulated by TMAO. Furthermore, TMAO obviously enhanced the phosphorylation of MAPK signaling molecules in vivo and in vitro. In conclusion, TMAO promotes the proliferation, migration and EMT of HCC cells by activating the MAPK pathway.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; MAPK; Migration; Proliferation; Trimethylamine N-oxide.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
