Pirfenidone inhibits TGF-β1-induced fibrosis via downregulation of Smad and ERK pathway in MDCK cells
- PMID: 39133399
- PMCID: PMC11442594
- DOI: 10.1007/s11259-024-10493-y
Pirfenidone inhibits TGF-β1-induced fibrosis via downregulation of Smad and ERK pathway in MDCK cells
Abstract
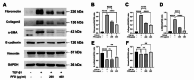
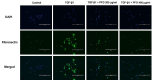
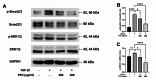
The prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in dogs increases with age, and renal fibrosis is an important pathophysiological mechanism in this process. However, only a few drugs that can effectively inhibit fibrosis in the kidneys of dogs are currently available. In this study, we aimed to determine whether pirfenidone, a drug that has shown antifibrotic effects in various clinical studies, also exerts antifibrotic effects on canine renal tubular epithelial cells, Madin-Darby canine kidney cells (MDCK). To this end, we treated MDCK cells with various concentrations of pirfenidone, followed by transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-β1) to stimulate fibrotic conditions. A cell viability assay was performed to determine the effect of pirfenidone on cell survival. Fibrosis-related markers and TGF-β1 fibrotic pathway-related markers were assessed using qPCR, Western blot analysis and immunocytochemistry. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed, followed by Tukey's post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. Pirfenidone treatment significantly reduced the expression of profibrotic markers such as α-smooth muscle actin, fibronectin, and collagen. Additionally, it upregulated the expression of E-cadherin, an epithelial marker. Furthermore, pirfenidone effectively inhibited the phosphorylation of key factors involved in the TGF-β1 signaling pathway, including Smad2/3 and ERK1/2. These results demonstrate that pirfenidone suppresses TGF-β1-induced fibrosis in MDCK cells by attenuating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the relevant signaling pathways.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Dog; Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; Pirfenidone; Renal fibrosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Microparticles derived from human erythropoietin mRNA-transfected mesenchymal stem cells inhibit epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and ameliorate renal interstitial fibrosis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Sep 29;11(1):422. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01932-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32993806 Free PMC article.
-
Pirfenidone inhibits transforming growth factor-β1-induced fibrogenesis by blocking nuclear translocation of Smads in human retinal pigment epithelial cell line ARPE-19.Mol Vis. 2012;18:1010-20. Epub 2012 Apr 21. Mol Vis. 2012. PMID: 22550395 Free PMC article.
-
[Modified Fangji Huangqi Decoction alleviates renal interstitial fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad/Snail signaling pathway during epithelial-mesenchymal transition].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Jun;49(11):3012-3020. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240204.402. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39041161 Chinese.
-
Central role of dysregulation of TGF-β/Smad in CKD progression and potential targets of its treatment.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 May;101:670-681. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.090. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29518614 Review.
-
Personalized Antifibrotic Therapy in CKD Progression.J Pers Med. 2024 Dec 5;14(12):1141. doi: 10.3390/jpm14121141. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39728054 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aresu L, Rastaldi MP, Scanziani E, Baily J, Radaelli E, Pregel P, Valenza F (2007) Epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) of renal tubular cells in canine glomerulonephritis. Virchows Arch 451(5):937–942. 10.1007/s00428-007-0482-8 - PubMed
-
- Benali SL, Lees GE, Castagnaro M, Aresu L (2014) Epithelial mesenchymal transition in the progression of renal disease in dogs. Histol Histopathol 29(11):1409–1414. 10.14670/HH-29.1409 - PubMed
-
- Bi L, Huang Y, Li J, Yang X, Hou G, Zhai P, Zhang Q, Alhaji AA, Yang Y, Liu B (2022) Pirfenidone attenuates renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis through inhibiting miR-21. Nephron 146(1):110–120. 10.1159/000519495 - PubMed
-
- Brook NR, Waller JR, Bicknell GR, Nicholson ML (2005) The experimental agent pirfenidone reduces pro-fibrotic gene expression in a model of tacrolimus-induced nephrotoxicity. J Surg Res 125(2):137–143. 10.1016/j.jss.2004.12.007 - PubMed
-
- Chen J-F, Ni H-F, Pan M-M, Liu H, Xu M, Zhang M-H, Liu B-C (2013) Pirfenidone inhibits macrophage infiltration in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 304(6):F676–F685. 10.1152/ajprenal.00507.2012 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

