Single-cell RNA sequencing comparison of CD4+, CD8+ and T-cell receptor γδ+ cutaneous T-cell lymphomas reveals subset-specific molecular phenotypes
- PMID: 39133553
- PMCID: PMC11758594
- DOI: 10.1093/bjd/ljae313
Single-cell RNA sequencing comparison of CD4+, CD8+ and T-cell receptor γδ+ cutaneous T-cell lymphomas reveals subset-specific molecular phenotypes
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Single-cell RNA sequencing comparison of CD4+, CD8+ and T-cell receptor γδ+ cutaneous T-cell lymphomas reveals subset-specific molecular phenotypes.Br J Dermatol. 2025 Feb 18;192(3):e2. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae374. Br J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39392468 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Malignant clones of primary cutaneous T-cell lymphomas (CTCL) can show a CD4+, CD8+ or T-cell receptor (TCR)-γδ+ phenotype, but their individual impact on tumour biology and skin lesion formation remains ill defined.
Objectives: To perform a comprehensive molecular characterization of CD4+ vs. CD8+ and TCR-γδ+ CTCL lesions.
Methods: We performed single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) of 18 CTCL skin biopsies to compare classic CD4+ advanced-stage mycosis fungoides (MF) with TCR-γ/δ+ MF and primary cutaneous CD8+ aggressive epidermotropic cytotoxic T-cell lymphoma (Berti lymphoma).
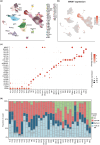
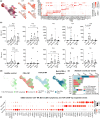
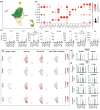
Results: Malignant clones of TCR-γ/δ+ MF and Bertilymphoma showed similar clustering patterns distinct from CD4+ MF, along with increased expression of cytotoxic markers such as NKG7, CTSW, GZMA and GZMM. Only advanced-stage CD4+ MF clones expressed central memory T-cell markers (SELL, CCR7, LEF1), alongside B1/B2 blood involvement, whereas TCR-γδ+ MF and Berti lymphoma harboured a more tissue-resident phenotype (CD69, CXCR4, NR4A1) without detectable cells in the blood. CD4+ MF and TCR-γδ+ MF skin lesions harboured strong type 2 immune activation across myeloid cells, while Berti lymphoma was more skewed toward type 1 immune responses. Both CD4+ MF and TCR-γδ+ MF lesions showed upregulation of keratinocyte hyperactivation markers such as S100A genes and KRT16. This increase was entirely absent in Berti lymphoma, possibly reflecting an aberrant keratinocyte response to invading tumour cells, which could contribute to the formation of the typical ulceronecrotic lesions within this entity.
Conclusions: Our scRNAseq profiling study reveals specific molecular patterns associated with distinct CTCL subtypes.
Plain language summary
Cutaneous T-cell lymphomas are a group of skin cancers characterized by an abnormal proliferation of a type of white blood cell called ‘T lymphocytes’. They consist of a diverse group of diseases, many of which are still poorly understood. Cancerous T lymphocytes in cutaneous lymphomas express the same T-cell receptor (TCR) sequence, hence the term ‘clones’ is often used to describe these malignant cells. Usually, these clonal T lymphocytes express an alpha/beta TCR in conjunction with protein called CD4. In rare cases, they may express an alpha/beta TCR along with a different protein called CD8, or instead display a gamma/delta TCR. To better understand these diseases, we compared three major subsets of cutaneous lymphomas (CD4+, CD8+, and TCR-gamma/delta) on a molecular level. We found specific signatures associated with each of the diseases, which may help with future strategies to better treat people with cutaneous T-cell lymphomas.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of British Association of Dermatologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: W.W. has received personal fees from LEO Pharma, Pfizer, Sanofi Genzyme, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Boehringer Ingelheim, AbbVie and Janssen. J.G. has received personal fees from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim and Novartis. C.J. has received personal fees from LEO Pharma, UCB Pharma, Pfizer, Recordati Rare Diseases, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Takeda, Kyowa Kirin, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, AbbVie, Janssen and Almirall. C.J. is an investigator for Eli Lilly, Novartis, Innate Pharma, AbbVie, Incyte, Boehringer Ingelheim and Almirall. P.M.B. has received personal fees from Almirall, Sanofi, Janssen, LEO Pharma, AbbVie, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, GSK, Regeneron, Eli Lilly, Celgene, Novartis, UCB, Merck, Galderma and BMS. P.M.B. is an investigator for Pfizer and Abbvie. P.M.B has also received research support from Pfizer (grant paid to his institution). The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Single-cell analyses of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma biopsies.Br J Dermatol. 2025 Jan 24;192(2):183. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae351. Br J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39271124 No abstract available.
References
-
- Latzka J, Assaf C, Bagot M et al. EORTC consensus recommendations for the treatment of mycosis fungoides/Sezary syndrome – update 2023. Eur J Cancer 2023; 195:113343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

