Liraglutide ameliorates inflammation and fibrosis by downregulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway in diabetic kidney disease
- PMID: 39133777
- PMCID: PMC11483077
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00083.2024
Liraglutide ameliorates inflammation and fibrosis by downregulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway in diabetic kidney disease
Abstract
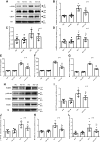
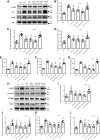
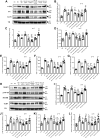
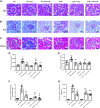
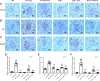
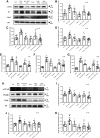
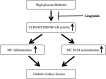
Inflammation and fibrosis play important roles in diabetic kidney disease (DKD). Previous studies have shown that glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists had renal protective effects. However, the mechanisms are not clear. The present study explored the effect of liraglutide (LR), a GLP-1R agonist, on the downregulation of glomerular inflammation and fibrosis in DKD by regulating the Toll-like receptor (TLR)4/myeloid differentiation marker 88 (MyD88)/nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway in mesangial cells (MCs). In vitro, rat MCs were cultured in high glucose (HG). We found that liraglutide treatment significantly reduced the HG-mediated activation of the TLR4/MYD88/NF-κB signaling pathway, extracellular matrix (ECM)-related proteins, and inflammatory factors. A combination of TLR4 inhibitor (TAK242) and liraglutide did not synergistically inhibit inflammatory factors and ECM proteins. Furthermore, in the presence of TLR4 siRNA, liraglutide significantly blunted HG-induced expression of fibronectin protein and inflammatory factors. Importantly, TLR4 selective agonist LPS or TLR4 overexpression eliminated the improvement effects of liraglutide on the HG-induced response. In vivo, administration of liraglutide for 8 wk significantly improved the glomerular damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice and reduced the expression of TLR4/MYD88/NF-κB signaling proteins, ECM protein, and inflammatory factors in renal cortex. TLR4-/- diabetic mice showed significant amelioration in urine protein excretion rate, glomerular pathological damage, inflammation, and fibrosis. Liraglutide attenuated glomerular hypertrophy, renal fibrosis, and inflammatory response in TLR4-/- diabetic mice. Taken together, our findings suggest that TLR4/MYD88/NF-κB signaling is involved in the regulation of inflammatory response and ECM protein proliferation in DKD. Liraglutide alleviates inflammation and fibrosis by downregulating the TLR4/MYD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in MCs.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA), has renoprotective effect in diabetic kidney disease (DKD). In DKD, TLR4/MYD88/NF-κB signaling is involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses and extracellular matrix (ECM) protein proliferation. Liraglutide attenuates renal inflammation and overexpression of ECM proteins by inhibiting TLR4/MYD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Therefore, we have identified a new mechanism that contributes to the renal protection of GLP-1RA, thus helping to design innovative treatment strategies for diabetic patients with various complications.
Keywords: TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB; diabetic kidney disease; extracellular matrix; inflammation; liraglutide.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

