Cabozantinib Plus Ipilimumab/Nivolumab in Patients With Previously Treated Advanced Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
- PMID: 39133806
- PMCID: PMC11834700
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgae512
Cabozantinib Plus Ipilimumab/Nivolumab in Patients With Previously Treated Advanced Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Erratum in
-
Correction to: "Cabozantinib Plus Ipilimumab/Nivolumab in Patients With Previously Treated Advanced Differentiated Thyroid Cancer".J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025 May 19;110(6):e2106. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaf185. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025. PMID: 40152435 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: This investigator-initiated phase II trial aimed to evaluate the efficacy of cabozantinib in combination with nivolumab and ipilimumab (CaboNivoIpi) in previously treated patients with radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer.
Methods: Eligible patients with radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer who progressed on 1 prior line of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-targeted therapy received a 2-week run-in of cabozantinib monotherapy followed by CaboNivoIpi for 4 cycles (cycle length = 6 weeks), followed by cabozantinib plus nivolumab (cycle length = 4 weeks) until disease progression. The primary endpoint was objective response rate (ORR) within the first 6 months of treatment. A Simon optimal 2-stage design allowed for an interim analysis after accrual of 10 evaluable patients. At least 5 responses were needed to proceed to stage 2.
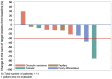
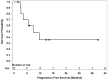
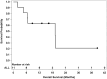
Results: Among 11 patients enrolled, the median age was 69 years. Prior vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-targeted therapies included lenvatinib, pazopanib, and sorafenib plus everolimus. Median follow-up was 7.9 months. Among 10 evaluable patients, ORR within the first 6 months of treatment was 10% (1 partial response). Median progression-free survival was 9 months (95% CI, 3.0-not reached) and median overall survival was 19.2 months (95% CI, 4.6-not reached). Grade 3/4 treatment-related adverse events (AEs) were noted in 55% (6/11) and grade 5 AEs in 18% (2/11) of patients. The most common treatment-related AE was hypertension. The study did not reach its prespecified efficacy threshold.
Conclusion: CaboNivoIpi had low ORRs and a high rate of grade ≥3 treatment-related AEs.
Clinical trial registration: NCT03914300.
Keywords: VEGFR; cabozantinib; differentiated thyroid cancer; immune checkpoint inhibitors; ipilimumab; nivolumab.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society. All rights reserved. For commercial re-use, please contact reprints@oup.com for reprints and translation rights for reprints. All other permissions can be obtained through our RightsLink service via the Permissions link on the article page on our site—for further information please contact journals.permissions@oup.com. See the journal About page for additional terms.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(1):7‐33. - PubMed
-
- Durante C, Haddy N, Baudin E, et al. Long-term outcome of 444 patients with distant metastases from papillary and follicular thyroid carcinoma: benefits and limits of radioiodine therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91(8):2892‐2899. - PubMed
-
- Schlumberger M, Tahara M, Wirth LJ, et al. Lenvatinib versus placebo in radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(7):621‐630. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 2UM1 CA186644-06/Moffitt Cancer Center
- 3UM1CA186686-03S1/Mayo Clinic, Rochester
- UM1 CA186712/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1CA186717/University of Southern California
- 4UM1CA186717-07/City of Hope Cancer Center
- UM1 CA186686/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA186717/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA186691/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1CA186691/Memorial Sloan Kettering
- 5UM1CA186712-03/The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center
- UM1 CA186644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

