Serum Levels of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 in Patients with Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 39134015
- PMCID: PMC11631035
- DOI: 10.1159/000540854
Serum Levels of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 in Patients with Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of the study was to investigate serum plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) levels of patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) and their relationship with clinical findings and treatment of disease.
Methods: The study included 125 PD patients and 48 healthy controls. Patients have been taking effective dopaminergic treatment regularly. The clinical severity of parkinsonism was assessed using the Hoehn and Yahr (HY) staging scale and the Unified PD Rating Scale (UPDRS). PAI-1 level analysis was performed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
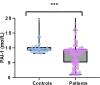
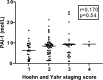
Results: Patients with PD had significantly lower serum PAI-1 levels than healthy controls (p < 0.001). Correlations with clinical findings showed only a marginally positive correlation between serum PAI-1 and HY score (r = 0.170, p = 0.05). In contrast, no significant correlation was demonstrated with the UPDRS score or other clinical parameters.
Conclusion: This is the first comprehensive analysis of serum PAI-1 levels in patients with PD. The distribution of PAI-1 in PD appears to be complex. The study results implicate that the paradoxical effects of tissue plasminogen activator on the brain parenchyma can be important in the pathophysiology of PD. Future studies are needed to elucidate the role of fibrinolytic system components in PD.
Keywords: Neurodegeneration; PAI-1; Parkinson’s disease; Serum.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Poewe W, Seppi K, Tanner CM, Halliday GM, Brundin P, Volkmann J, et al. Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17013. - PubMed
-
- Michel PP, Hirsch EC, Hunot S. Understanding dopaminergic cell death pathways in Parkinson disease. Neuron. 2016;90(4):675–91. - PubMed
-
- Nolan YM, Sullivan AM, Toulouse A. Parkinson’s disease in the nuclear age of neuroinflammation. Trends Mol Med. 2013;19(3):187–96. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous