Epithelium/imcDC2 axis facilitates the resistance of neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 in human NSCLC
- PMID: 39134346
- PMCID: PMC11332012
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007854
Epithelium/imcDC2 axis facilitates the resistance of neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 in human NSCLC
Abstract
Background: Therapeutic resistance is a main obstacle to achieve long-term benefits from immune checkpoint inhibitors. The underlying mechanism of neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 resistance remains unclear.
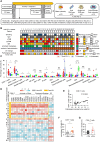
Methods: Multi-omics analysis, including mass cytometry, single-cell RNA-seq, bulk RNA-seq, and polychromatic flow cytometry, was conducted using the resected tumor samples in a cohort of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients received neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 therapy. Tumor and paired lung samples acquired from treatment-naïve patients were used as a control. In vitro experiments were conducted using primary cells isolated from fresh tissues and lung cancer cell lines. A Lewis-bearing mouse model was used in the in vivo experiment.
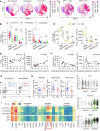
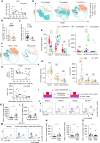
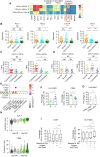
Results: The quantity, differentiation status, and clonal expansion of tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cells (CD8+ TRMs) are positively correlated with therapeutic efficacy of neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 therapy in human NSCLC. In contrast, the quantity of immature CD1c+ classical type 2 dendritic cells (imcDC2) and galectin-9+ cancer cells is negatively correlated with therapeutic efficacy. An epithelium/imDC2 suppressive axis that restrains the antitumor response of CD8+ TRMs via galectin-9/TIM-3 was uncovered. The expression level of CD8+ TRMs and galectin-9+ cancer cell-related genes predict the clinical outcome of anti-PD-1 neoadjuvant therapy in human NSCLC patients. Finally, blockade of TIM-3 and PD-1 could improve the survival of tumor-bearing mouse by promoting the antigen presentation of imcDC2 and CD8+ TRMs-mediated tumor-killing.
Conclusion: Galectin-9 expressing tumor cells sustained the primary resistance of neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 therapy in NSCLC through galectin-9/TIM-3-mediated suppression of imcDC2 and CD8+ TRMs. Supplement of anti-TIM-3 could break the epithelium/imcDC2/CD8+ TRMs suppressive loop to overcome anti-PD-1 resistance.
Trial registration number: NCT03732664.
Keywords: CD8-Positive T-Lymphocytes; Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors; Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



References
-
- Sharma P, Siddiqui BA, Anandhan S, et al. The Next Decade of Immune Checkpoint Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:838–57. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1680. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
