Biodegradation of Water-Soluble Polymers by Wastewater Microorganisms: Challenging Laboratory Testing Protocols
- PMID: 39134471
- PMCID: PMC11360367
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.4c05808
Biodegradation of Water-Soluble Polymers by Wastewater Microorganisms: Challenging Laboratory Testing Protocols
Abstract
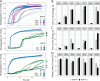
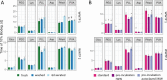
For water-soluble polymers (WSPs) that enter environmental systems at their end-of-life, biodegradability is a key functionality. For the development and regulation of biodegradable WSPs, testing methods that are both scientifically validated and economically practicable are needed. Here, we used respirometric laboratory tests to study the biodegradation of poly(amino acids), poly(ethylene glycol), and poly(vinyl alcohol), together with appropriate low-molecular-weight reference substrates. We varied key protocol steps of commonly used testing methods, which were originally established for small molecules and tested for effects on WSP biodegradation. We found that avoiding aeration of the wastewater inoculate prior to WSP addition, incubating WSP with filter-sterilized wastewater prior to biodegradation testing, and lowering the WSP concentration can increase biodegradation rates of WSPs. Combining the above-mentioned protocol variations substantially affected the results of the biodegradation testing for the two poly(amino acids) tested herein (i.e., poly(lysine) and poly(aspartic acid)). Our findings were consistent between microbial inocula derived from two municipal wastewater treatment plants. Our study presents promising biodegradation dynamics for poly(amino acids) and highlights the importance, strengths, and limitations of respirometric laboratory methods for WSP biodegradation testing.
Keywords: Water-soluble polymers; biodegradation testing; biological wastewater treatment; environmentally benign-by-design.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): S.D. and G.B. work at BASF SE, a company producing and marketing polymers. A.K. and M.Z. declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Vandermeulen G. W.; Boarino A.; Klok H.-A. Biodegradation of Water-soluble and Water-dispersible Polymers for Agricultural, Consumer, and Industrial Applications—Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Materials Solutions. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 60, 1797. 10.1002/pol.20210922. - DOI
-
- Polymers in Liquid Formulations Technical Report: A Landscape View of the Global PLFs Market. Royal Society of Chemistry.https://www.rsc.org/globalassets/22-new-perspectives/sustainability/liqu... (accessed 2024-02-01).
-
- Pauelsen F.; Huppertsberg S.; Knepper T. P.; Zahn D. Narrowing the Analytical Gap for Water-Soluble Polymers: A Novel Trace-Analytical Method and First Quantitative Occurrence Data for Polyethylene Oxide in Surface and Wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163563 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163563. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

