Prognostic impact of post-transplant diabetes mellitus in kidney allograft recipients: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 39134508
- PMCID: PMC11879034
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfae185
Prognostic impact of post-transplant diabetes mellitus in kidney allograft recipients: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Post-transplant diabetes mellitus (PTDM) is a complex condition arising from various factors including immunosuppressive medications, insulin resistance, impaired insulin secretion and inflammatory processes. Its impact on patient and graft survival is a significant concern in kidney transplant recipients. PTDM's impact on kidney transplant recipients, including patient and graft survival and cardiovascular mortality, is a significant concern, given conflicting findings in previous studies. This meta-analysis was imperative not only to incorporate emerging evidence but also to delve into cause-specific mortality considerations. We aimed to comprehensively evaluate the association between PTDM and clinical outcomes, including all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, sepsis-related mortality, malignancy-related mortality and graft loss, in kidney transplant recipients.
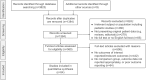
Methods: PubMed, Ovid/Medline, Web of Science, Scopus and Cochrane Library databases were screened and studies evaluating the effect of PTDM on all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, sepsis-related mortality, malignancy-related mortality and overall graft loss in adult kidney transplant recipients were included.
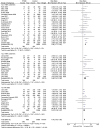
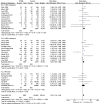
Results: Fifty-three studies, encompassing a total of 138 917 patients, evaluating the association between PTDM and clinical outcomes were included. Our analysis revealed a significant increase in all-cause mortality [risk ratio (RR) 1.70, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.53 to 1.89, P < .001] and cardiovascular mortality (RR 1.86, 95% CI 1.36 to 2.54, P < .001) among individuals with PTDM. Moreover, PTDM was associated with a higher risk of sepsis-related mortality (RR 1.96, 95% CI 1.51 to 2.54, P < .001) but showed no significant association with malignancy-related mortality (RR 1.20, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.88). Additionally, PTDM was linked to an increased risk of overall graft failure (RR 1.33, 95% CI 1.16 to 1.54, P < .001).
Conclusion: These findings underscore the importance of comprehensive management strategies and the need for research targeting PTDM to improve outcomes in kidney transplant recipients.
Keywords: graft loss; kidney transplantation; mortality; new onset diabetes after transplantation; post-transplant diabetes mellitus.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Conflict of interest statement
K.T. is supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) research grants R01MD014712, U2CDK114886, UL1TR002319, U54DK083912, U01DK100846, OT2HL161847, UM1AI109568 and OT2OD032581, and CDC project numbers 75D301-21-P-12254 and 75D301-23-C-18264. She has also received investigator-initiated grant support from Travere, Bayer, and the Doris Duke Foundation outside of the submitted work. She reports consultancy fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly and Company, and Novo Nordisk, and speaker fees from Novo Nordisk. The other authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
"Effect of post-kidney transplant diabetes mellitus on long-term outcomes in a cohort of pediatric kidney transplant recipients from 2005 to 2022." Survival analysis.BMJ Paediatr Open. 2024 Dec 24;8(1):e002710. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2024-002710. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2024. PMID: 39725454 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of post-transplant diabetes mellitus on liver transplant outcomes.Clin Transplant. 2019 Jun;33(6):e13554. doi: 10.1111/ctr.13554. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Clin Transplant. 2019. PMID: 30927288 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparing survival outcomes for kidney transplant recipients with pre-existing diabetes versus those who develop post-transplantation diabetes.Diabet Med. 2022 Feb;39(2):e14707. doi: 10.1111/dme.14707. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Diabet Med. 2022. PMID: 34599527
-
An update review of post-transplant diabetes mellitus: Concept, risk factors, clinical implications and management.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024 Jul;26(7):2531-2545. doi: 10.1111/dom.15575. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024. PMID: 38558257 Review.
-
Post-transplant diabetes mellitus.J Nephrol. 2003 Sep-Oct;16(5):626-34. J Nephrol. 2003. PMID: 14733407 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

