Gefitinib (an EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor) plus anlotinib (an multikinase inhibitor) for untreated, EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small cell lung cancer (FL-ALTER): a multicenter phase III trial
- PMID: 39134529
- PMCID: PMC11319491
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-024-01927-9
Gefitinib (an EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor) plus anlotinib (an multikinase inhibitor) for untreated, EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small cell lung cancer (FL-ALTER): a multicenter phase III trial
Abstract
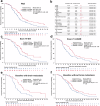
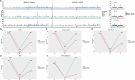
Dual inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling pathways offers the prospect of improving the effectiveness of EFGR-targeted therapy. In this phase 3 study (ClinicalTrial.gov: NCT04028778), 315 patients with treatment-naïve, EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) were randomized (1:1) to receive anlotinib or placebo plus gefitinib once daily on days 1-14 per a 3-week cycle. At the prespecified final analysis of progression-free survival (PFS), a significant improvement in PFS was observed for the anlotinib arm over the placebo arm (hazards ratio [HR] = 0.64, 95% CI, 0.48-0.80, P = 0.003). Particularly, patients with brain metastasis and those harboring EGFR amplification or high tumor mutation load gained significant more benefits in PFS from gefitinib plus anlotinib. The incidence of grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events was 49.7% of the patients receiving gefitinib plus anlotinib versus 31.0% of the patients receiving gefitinib plus placebo. Anlotinib plus gefitinib significantly improves PFS in patients with treatment-naïve, EGFR-mutated, advanced NSCLC, with a manageable safety profile.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
L.Z. has received research support from Chia Tai Tianqing Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Roche, and Bristol-Myers Squibb. Other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Akamatsu, H. et al. Efficacy of Osimertinib Plus Bevacizumab vs Osimertinib in Patients With EGFR T790M-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Previously Treated With Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor: West Japan Oncology Group 8715L Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol.7, 386–394 (2021). 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.6758 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

