Network analysis to identify driver genes and combination drugs in brain cancer
- PMID: 39134610
- PMCID: PMC11319350
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-69705-9
Network analysis to identify driver genes and combination drugs in brain cancer
Abstract
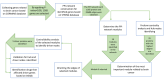
Brain cancer is one of the deadliest diseases, although many efforts have been made to treat it, there is no comprehensive and effective treatment approach yet. In recent years, the use of network-based analysis to identify important biological genes and pathways involved in various complex diseases, including brain cancer, has attracted the attention of researchers. The goal of this manuscript is to perform a comprehensive analysis of the various results presented related to brain cancer. For this purpose, firstly, based on the CORMINE medical database, collected all the genes related to brain cancer with a valid P-value. Then the structural and functional relationships between the above gene sets have been identified based on the STRING database. Next, in the PPI network, hub centrality analysis was performed to determine the proteins that have many connections with other proteins. After the modularization of the network, the module with the most hub vertices is considered as the most relevant module to the formation and progression of brain cancer. Since the driver vertices play an important role in biological systems, the edges of the selected module were oriented, and by analyzing the controllability of complex networks, a set of five proteins with the highest control power has been identified. Finally, based on the drug-gene interaction, a set of drugs effective on each of the driver genes has been obtained, which can potentially be used as new combination drugs. Validation of the hub and driver proteins shows that they are mainly essential proteins in the biological processes related to the various cancers and therefore the drugs that affect them can be considered as new combination therapy. The presented procedure can be used for any other complex disease.
Keywords: Brain cancer; Controllability; Driver gene; Hub proteins; Network; Systems biology.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrated bioinformatics analysis for the screening of hub genes and therapeutic drugs in ovarian cancer.J Ovarian Res. 2020 Jan 27;13(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13048-020-0613-2. J Ovarian Res. 2020. PMID: 31987036 Free PMC article.
-
Computational screening of potential glioma-related genes and drugs based on analysis of GEO dataset and text mining.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 26;16(2):e0247612. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247612. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33635875 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Driver Genes and Interaction Networks Related to Brain Metastasis in Breast Cancer Patients.Dis Markers. 2022 Jan 28;2022:7631456. doi: 10.1155/2022/7631456. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35132338 Free PMC article.
-
Gene network in pulmonary tuberculosis based on bioinformatic analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Aug 18;20(1):612. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05335-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32811479 Free PMC article.
-
Systems biology approaches to identify driver genes and drug combinations for treating COVID-19.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 26;14(1):2257. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52484-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38278931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Masoudi-Nejad, A., Bidkhori, G., Ashtiani, S. H., Najafi, A., Bozorgmehr, J. H. & Wang, E. in Seminars in Cancer Biology. 60–69 (Elsevier). - PubMed
-
- Vasciaveo, A. et al. OncoLoop: A network-based precision cancer medicine framework. Cancer Discov.13, 386–409 (2023). 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-0342 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maiorov, E. G., Keskin, O., Gursoy, A. & Nussinov, R. in Seminars in Cancer Biology. 243–251 (Elsevier). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical