Quantitative analysis of dose dependent DNA fragmentation in dry pBR322 plasmid using long read sequencing and Monte Carlo simulations
- PMID: 39134627
- PMCID: PMC11319478
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-69406-3
Quantitative analysis of dose dependent DNA fragmentation in dry pBR322 plasmid using long read sequencing and Monte Carlo simulations
Abstract
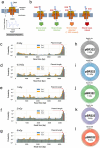
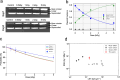
Exposure to ionizing radiation can induce genetic aberrations via unrepaired DNA strand breaks. To investigate quantitatively the dose-effect relationship at the molecular level, we irradiated dry pBR322 plasmid DNA with 3 MeV protons and assessed fragmentation yields at different radiation doses using long-read sequencing from Oxford Nanopore Technologies. This technology applied to a reference DNA model revealed dose-dependent fragmentation, as evidenced by read length distributions, showing no discernible radiation sensitivity in specific genetic sequences. In addition, we propose a method for directly measuring the single-strand break (SSB) yield. Furthermore, through a comparative study with a collection of previous works on dry DNA irradiation, we show that the irradiation protocol leads to biases in the definition of ionizing sources. We support this scenario by discussing the size distributions of nanopore sequencing reads in the light of Geant4 and Geant4-DNA simulation toolkit predictions. We show that integrating long-read sequencing technologies with advanced Monte Carlo simulations paves a promising path toward advancing our comprehension and prediction of radiation-induced DNA fragmentation.
Keywords: DNA damages; Ionizing radiation; Monte Carlo simulation; Nanopore sequencing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MPEXS-DNA, a new GPU-based Monte Carlo simulator for track structures and radiation chemistry at subcellular scale.Med Phys. 2019 Mar;46(3):1483-1500. doi: 10.1002/mp.13370. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Med Phys. 2019. PMID: 30593679 Free PMC article.
-
On the consistency of Monte Carlo track structure DNA damage simulations.Med Phys. 2014 Dec;41(12):121708. doi: 10.1118/1.4901555. Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 25471955
-
Impact of Ultra-High-Dose-Rate Irradiation on DNA: Single-Strand Breaks and Base Damage.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 20;26(5):1800. doi: 10.3390/ijms26051800. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076429 Free PMC article.
-
Track structure modeling in liquid water: A review of the Geant4-DNA very low energy extension of the Geant4 Monte Carlo simulation toolkit.Phys Med. 2015 Dec;31(8):861-874. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2015.10.087. Epub 2015 Dec 1. Phys Med. 2015. PMID: 26653251 Review.
-
Track structure in radiation biology: theory and applications.Int J Radiat Biol. 1998 Apr;73(4):355-64. doi: 10.1080/095530098142176. Int J Radiat Biol. 1998. PMID: 9587072 Review.
References
-
- UNSCEAR 2008 Report Volume I. United Nations: Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation.www.unscear.org/unscear/en/publications/2008_1.html.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

