Whole brain radiation therapy for patients with brain metastases: survival outcomes and prognostic factors in a contemporary institutional series
- PMID: 39134688
- PMCID: PMC11527910
- DOI: 10.1007/s00066-024-02275-x
Whole brain radiation therapy for patients with brain metastases: survival outcomes and prognostic factors in a contemporary institutional series
Abstract
Purpose: To study survival outcomes and prognostic factors in patients undergoing whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) for brain metastases in the contemporary setting.
Methods: Patients undergoing WBRT from 2013-2021 were retrospectively included in an ethics-approved institutional database. Patient and treatment characteristics were assessed, including patient age, primary tumor histology, Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS), extracranial disease, as well as WBRT dose. Overall survival (OS) was calculated from onset of WBRT using the Kaplan-Meier method.
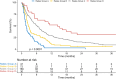
Results: A total of 328 patients (median age 63 years) were included. Most patients (52%) had ≥ 10 brain metastases, and 17% had leptomeningeal disease. WBRT was delivered with 10 × 3 Gy (64%), 5 × 4 Gy (25%), or other regimens (11%). Median follow-up was 4.4 months (range, 0.1-154.3), and median OS was 4.7 months (95%CI, 3.8-6.0). OS differed between histologies (p = 0.01), with the longest survival seen in breast cancer (median 7.7 months). Patients with KPS of 90-100 survived for a median of 8.3 months, compared to 4.1 months with KPS 70-80, and 1.7 months with KPS < 70 (p < 0.01). Multivariate analyses revealed that KPS had the largest impact on survival. Patients who received a WBRT dose of ≥ 30 Gy also had a reduced risk of death (HR 0.45; p < 0.001). Survival differed between subgroups reclassified according to the Rades scoring system (p < 0.01).
Conclusion: Survival outcomes of patients undergoing WBRT in the contemporary era appear comparable to historical cohorts, although individual patient factors need to be considered. Patients with otherwise favorable prognostic factors may benefit from longer-course WBRT.
Keywords: Brain metastases; WBRT; Whole brain radiation therapy; Whole brain radiotherapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A. Estermann, C. Schneider, F. Zimmermann, A. Papachristofilou and T. Finazzi declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Gavrilovic IT, Posner JB (2005) Brain metastases: epidemiology and pathophysiology. J Neurooncol 75:5–14. 10.1007/s11060-004-8093-6 - PubMed
-
- Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Sloan AE, Davis FG, et al (2004) Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 22:2865–2872. 10.1200/JCO.2004.12.149 - PubMed
-
- Pease NJ, Edwards A, Moss LJ (2005) Effectiveness of whole brain radiotherapy in the treatment of brain metastases: a systematic review. Palliat Med 19:288–299. 10.1191/0269216305pm1017oa - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

