Virtual crossmatching reveals upregulation of placental HLA-Class II in chronic histiocytic intervillositis
- PMID: 39134702
- PMCID: PMC11319473
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-69315-5
Virtual crossmatching reveals upregulation of placental HLA-Class II in chronic histiocytic intervillositis
Abstract
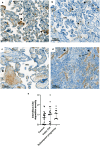
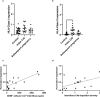
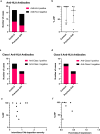
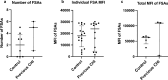
Chronic histiocytic intervillositis (CHI) is a recurrent placental lesion where maternal macrophages infiltrate the intervillous space. Its cause is unknown, though due to similarities to rejected allografts one hypothesis is that CHI represents maternal-fetal rejection. Here, virtual crossmatching was applied to healthy pregnancies and those with a history of CHI. Anti-HLA antibodies, measured by Luminex, were present in slightly more controls than CHI (8/17 (47.1%) vs 5/14 (35.7%)), but there was no significant difference in levels of sensitisation or fetal specific antibodies. Quantification of immunohistochemical staining for HLA-Class II was increased in syncytiotrophoblast of placentas with CHI (Grade 0.44 [IQR 0.1-0.7]) compared to healthy controls (0.06 [IQR 0-0.2]) and subsequent pregnancies (0.13 [IQR 0-0.3]) (P = 0.0004). HLA-Class II expression was positively related both to the severity of CHI (r = 0.67) and C4d deposition (r = 0.48). There was no difference in overall C4d and HLA-Class I immunostaining. Though increased anti-HLA antibodies were not evident in CHI, increased expression of HLA-Class II at the maternal-fetal interface suggests that they may be relevant in its pathogenesis. Further investigation of antibodies immediately after diagnosis is warranted in a larger cohort of CHI cases to better understand the role of HLA in its pathophysiology.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Rodger JC, Drake BL. The Enigma of the Fetal Graft. Am Sci. 1987;75: 51–57. Available: http://www.jstor.org/stable/27854450
-
- Apps, R. et al. Human leucocyte antigen (HLA) expression of primary trophoblast cells and placental cell lines, determined using single antigen beads to characterize allotype specificities of anti-HLA antibodies. Immunology127, 26–39. 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.03019.x (2009). 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.03019.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Somerset, D. A., Zheng, Y., Kilby, M. D., Sansom, D. M. & Drayson, M. T. Normal human pregnancy is associated with an elevation in the immune suppressive CD25+ CD4+ regulatory T-cell subset. Immunology112, 38–43. 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01869.x (2004). 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01869.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

