Effectiveness and safety of rituximab in severely relapsed antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: a retrospective analysis of a Japanese multicentre cohort from the J-CANVAS
- PMID: 39134873
- PMCID: PMC11442524
- DOI: 10.1007/s10067-024-07096-y
Effectiveness and safety of rituximab in severely relapsed antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: a retrospective analysis of a Japanese multicentre cohort from the J-CANVAS
Abstract
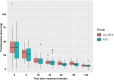
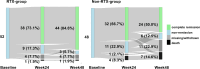
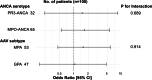
We aimed to clarify the long-term safety and efficacy of rituximab (RTX) as a remission induction therapy following severe relapse in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV). We retrospectively collected the data of patients with severely relapsed AAV from a Japanese multicentre cohort. The primary exposure was RTX use; the primary outcome was complete remission (CR) proportions at week 24. Baseline characteristics were compared between the RTX and non-RTX groups. We performed multivariate logistic regression analysis and one-to-one propensity score matching analysis as a sensitivity analysis. Totally, 100 patients were enrolled: 52 in the RTX group and 48 in the non-RTX group. Baseline characteristics were comparable between the two groups, except for age, AAV subtype and ANCA serotype. The median age was 71 vs. 75 years, and the PR3-ANCA positivity rate was 44.2% vs. 18.8% in the RTX and non-RTX groups, respectively. No significant difference was observed in CR proportions at week 24 between the two groups (79.2% vs. 68.1%, p = 0.321), with an adjusted odds ratio of 1.27 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.47-3.51). At week 48, CR proportions were significantly higher in the RTX group (91.7% vs. 64.9%, p = 0.005), with an adjusted odds ratio of 2.95 (95% CI 0.97-9.91). Serious infection rates were lower in the RTX group than in the non-RTX group, with no statistically significant difference. RTX was not superior to conventional immunosuppressive therapies at week 24 but showed significantly favourable results at week 48 for severely relapsed AAV.
Keywords: ANCA-associated vasculitis; Granulomatosis with polyangiitis; Microscopic polyangiitis; Relapse; Rituximab.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We disclose the following conflicts of interest with pharmaceutical companies promoting RTX or RTX biosimilars as outlined below. Yusuke Yoshida: speaker fees — Chugai. Takashi Kida: speaker fees — Chugai. Daiki Nakagomi: scholarship donations, speaker fees — Chugai. Naoho Takizawa: speaker fees — Chugai, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Pfizer. Yuji Kukida: speaker fees — Chugai, Pfizer. Kiyoshi Matsui: research grants — Chugai. Masaru Kato: speaker fees — Chugai, Pfizer. Tomoaki Takata: speaker fees — Chugai; scholarship donations, speaker fees — Kyowa Hakko Kirin. Takafumi Ito: speaker fees — Chugai, Kyowa Hakko Kirin. Takashi Kawaguchi: speaker fees, consultancy — Chugai; speaker fees — Kyowa Hakko Kirin. Yutaka Kawahito: speaker fees, research grants — Chugai; speaker fees — Pfizer. Shintaro Hirata: speaker fees, consultancy fees, research grants — Chugai, Pfizer and additional relationships, including speaker fees, consultancy fees, research grants and honoraria with AbbVie; Asahi — Kasei Pharma; Astellas; AstraZeneca; Ayumi; Bristol Myers Squibb; Boehringer Ingelheim; Daiichi — Sankyo; Eisai; Gilead Sciences; GlaxoSmithKline; Eli Lilly; Janssen; Nippon Shinyaku; Novartis; Otsuka; Taisho; Tanabe — Mitsubishi; and UCB.
Figures
References
-
- Kitching AR, Anders HJ, Basu N et al (2020) ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 6:71. 10.1038/s41572-020-0204-y - PubMed
-
- Nakazawa D, Masuda S, Tomaru U, Ishizu A (2019) Pathogenesis and therapeutic interventions for ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 15:91–101. 10.1038/s41584-018-0145-y - PubMed
-
- McClure M, Gopaluni S, Jayne D, Jones R (2018) B cell therapy in ANCA-associated vasculitis: current and emerging treatment options. Nat Rev Rheumatol 14:580–591. 10.1038/s41584-018-0065-x - PubMed
-
- Nagasaka K, Amano K, Dobashi H et al (2023) Nation-wide cohort study of remission induction therapy using rituximab in Japanese patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis: effectiveness and safety in the first 6 months. Mod Rheumatol 33:1117–1124. 10.1093/mr/roac150 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

