Contextual factors and G6PD diagnostic testing: a scoping review and evidence and gap map
- PMID: 39135005
- PMCID: PMC11318274
- DOI: 10.1186/s12936-024-05050-6
Contextual factors and G6PD diagnostic testing: a scoping review and evidence and gap map
Abstract
Background: Testing for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency is an important consideration regarding treatment for malaria. G6PD deficiency may lead to haemolytic anaemia during malaria treatment and, therefore, determining G6PD deficiency in malaria treatment strategies is extremely important.
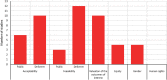
Methods: This report presents the results of a scoping review and evidence and gap map for consideration by the Guideline Development Group for G6PD near patient tests to support radical cure of Plasmodium vivax. This scoping review has investigated common diagnostic tests for G6PD deficiency and important contextual and additional factors for decision-making. These factors include six of the considerations recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) handbook for guideline development as important to determining the direction and strength of a recommendation, and included 'acceptability', 'feasibility,' 'equity,' 'valuation of outcomes,' 'gender' and 'human rights'. The aim of this scoping review is to inform the direction of future systematic reviews and evidence syntheses, which can then better inform the development of WHO recommendations regarding the use of G6PD deficiency testing as part of malaria treatment strategies.
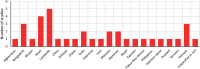
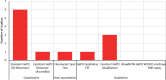
Results: A comprehensive search was performed, including published, peer-reviewed literature for any article, of any study design and methodology that investigated G6PD diagnostic tests and the factors of 'acceptability', 'feasibility,' 'equity,' 'valuation of outcomes,' 'gender' and 'human rights'. There were 1152 studies identified from the search, of which 14 were determined to be eligible for inclusion into this review. The studies contained data from over 21 unique countries that had considered G6PD diagnostic testing as part of a malaria treatment strategy. The relationship between contextual and additional factors, diagnostic tests for G6PD deficiency and study methodology is presented in an overall evidence and gap, which showed that majority of the evidence was for the contextual factors for diagnostic tests, and the 'Standard G6PD (SD Biosensor)' test.
Conclusions: This scoping review has produced a dynamic evidence and gap map that is reactive to emerging evidence within the field of G6PD diagnostic testing. The evidence and gap map has provided a comprehensive depiction of all the available literature that address the contextual and additional factors important for decision-making, regarding specific G6PD diagnostic tests. The majority of data available investigating the contextual factors of interest relates to quantitative G6PD diagnostic tests. While a formal qualitative synthesis of this data as part of a systematic review is possible, the data may be too heterogenous for this to be appropriate. These results can now be used to inform future direction of WHO Guideline Development Groups for G6PD near patient tests to support radical cure of P. vivax malaria.
Keywords: Contextual factors; Evidence; G6PD; Gaps; Malaria; Mapping; Scoping review.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
This work is funded by the World Health Organization, APW203270267. All rights in all work performed under this APW, including, without limitation, the report and database, shall be vested in WHO. The Contractual Partner can present and discuss work undertaken under this agreement in university seminars, tutorials, and lectures, but will need to inform WHO of any specific plans to do so and share the materials that will be presented.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Implementing radical cure diagnostics for malaria: user perspectives on G6PD testing in Bangladesh.Malar J. 2021 May 12;20(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s12936-021-03743-w. Malar J. 2021. PMID: 33980257 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of G6PD diagnostic test for Plasmodium vivax radical cure in Lao PDR: An economic modelling study.PLoS One. 2022 Apr 25;17(4):e0267193. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267193. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35468145 Free PMC article.
-
G6PD testing and radical cure for Plasmodium vivax in Cambodia: A mixed methods implementation study.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 20;17(10):e0275822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275822. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36264996 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges for achieving safe and effective radical cure of Plasmodium vivax: a round table discussion of the APMEN Vivax Working Group.Malar J. 2017 Apr 5;16(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s12936-017-1784-1. Malar J. 2017. PMID: 28381261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of primaquine and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency testing: Divergent policies and practices in malaria endemic countries.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 Apr 19;12(4):e0006230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006230. eCollection 2018 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 29672516 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic accuracy of the point-of-care standard G6PD test™ (SD Biosensor) for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Malar J. 2024 Nov 2;23(1):327. doi: 10.1186/s12936-024-05144-1. Malar J. 2024. PMID: 39488711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Handbook for guideline development. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

