Lipid profile alterations and biomarker identification in type 1 diabetes mellitus patients under glycemic control
- PMID: 39135021
- PMCID: PMC11318335
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-024-01679-1
Lipid profile alterations and biomarker identification in type 1 diabetes mellitus patients under glycemic control
Abstract
Background: Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is well-known to trigger a disruption of lipid metabolism. This study aimed to compare lipid profile changes in T1DM patients after achieving glucose control and explore the underlying mechanisms. In addition, we seek to identify novel lipid biomarkers associated with T1DM under conditions of glycemic control.
Methods: A total of 27 adults with T1DM (age: 34.3 ± 11.2 yrs) who had maintained glucose control for over a year, and 24 healthy controls (age: 35.1 + 5.56 yrs) were recruited. Clinical characteristics of all participants were analyzed and plasma samples were collected for untargeted lipidomic analysis using mass spectrometry.
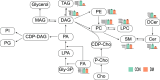
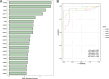
Results: We identified 594 lipid species from 13 major classes. Differential analysis of plasma lipid profiles revealed a general decline in lipid levels in T1DM patients with controlled glycemic levels, including a notable decrease in triglycerides (TAGs) and diglycerides (DAGs). Moreover, these T1DM patients exhibited lower levels of six phosphatidylcholines (PCs) and three phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs). Random forest analysis determined DAG(14:0/20:0) and PC(18:0/20:3) to be the most prominent plasma markers of T1DM under glycemic control (AUC = 0.966).
Conclusions: The levels of all metabolites from the 13 lipid classes were changed in T1DM patients under glycemic control, with TAGs, DAGs, PCs, PEs, and FFAs demonstrating the most significant decrease. This research identified DAG(14:0/20:0) and PC(18:0/20:3) as effective plasma biomarkers in T1DM patients with controled glycemic levels.
Keywords: Biomarker; Diglyceride; Glycemic control; Lipidomic profiling; Triglyceride; Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lipidomic profiling of plasma free fatty acids in type-1 diabetes highlights specific changes in lipid metabolism.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2021 Jan;1866(1):158823. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158823. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2021. PMID: 33010452 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating metabolomic and lipidomic changes in subjects with new-onset type 1 diabetes after optimization of glycemic control.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2023 Mar;197:110578. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110578. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2023. PMID: 36804334
-
Deep serum lipidomics identifies evaluative and predictive biomarkers for individualized glycemic responses following low-energy diet-induced weight loss: a PREVention of diabetes through lifestyle Intervention and population studies in Europe and around the World (PREVIEW) substudy.Am J Clin Nutr. 2024 Oct;120(4):864-878. doi: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2024.08.015. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Am J Clin Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39182617
-
Influence of Anaerobic Exercise in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Biomarkers: ASystematic Review.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024;20(9):e230124226018. doi: 10.2174/0115733998274125231126111321. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024. PMID: 38275039
-
Is Helicobacter pylori infection associated with glycemic control in diabetics?World J Gastroenterol. 2015 May 7;21(17):5407-16. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i17.5407. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25954115 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pre-Type 1 Diabetes in Adolescents and Teens: Screening, Nutritional Interventions, Beta-Cell Preservation, and Psychosocial Impacts.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 9;14(2):383. doi: 10.3390/jcm14020383. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39860389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) does not affect whole blood responses to alginate-based microspheres despite plasma lipid and glucose differences.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jul 18;34:102113. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102113. eCollection 2025 Oct. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40755902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raile K, Galler A, Hofer S, Herbst A, Dunstheimer D, Busch P, Holl RW. Diabetic nephropathy in 27,805 children, adolescents, and adults with type 1 diabetes: effect of diabetes duration, A1C, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes onset, and sex. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(10):2523–8. 10.2337/dc07-0282 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- L-201624/Training Project for Leading Talents of the Health and Family Planning Commission of Yunnan Province
- DKME202218/Key Laboratory of Diabetes Immunology, Ministry of Education, National Clinical Research Center for Metabolic Diseases open project
- N2020LCZXKF-NM06/Yunnan Clinical Medical Research Center open project
- YNWR-MY-2019-020/Special Project for "Famous Doctor" of Yunnan Ten Thousand Talents Plan
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

