Upregulation of MELK promotes chemoresistance and induces macrophage M2 polarization via CSF-1/JAK2/STAT3 pathway in gastric cancer
- PMID: 39135038
- PMCID: PMC11320770
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-024-03453-8
Upregulation of MELK promotes chemoresistance and induces macrophage M2 polarization via CSF-1/JAK2/STAT3 pathway in gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: Gastric cancer (GC) stands out as one of the most prevalent malignancies affecting the digestive system, characterized by a substantial incidence rate and mortality. Maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase (MELK) has been implicated in the advancement of various cancer types and the modulation of the tumor microenvironment. This study aims to delve into the involvement of MELK in chemoresistance and the tumor microenvironment of GC.
Methods: The MELK expression was detected using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), western blotting and immunohistochemistry. Lentiviral transfection was employed to establish stable cell lines with either overexpressed or silenced MELK. The impact of MELK on the chemoresistance of GC cells and the polarization of macrophages was investigated through in vitro and in vivo functional assays. Additionally, the correlation between MELK and the cytokines colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1), as well as stromal macrophages, was analysed. The prognostic significance of MELK, CSF-1, and CD206 expression levels in clinical samples was further investigated.
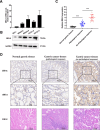
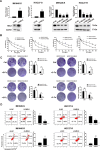
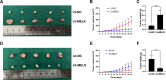
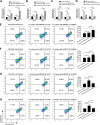
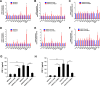
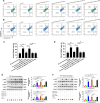
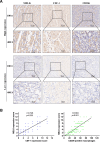
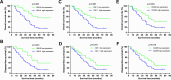
Results: MELK was found to be highly expressed in chemoresistant GC cells and tissues. Furthermore, both in vitro and in vivo assays indicated that MELK overexpression conferred chemoresistance in GC cells. Additionally, MELK overexpression was observed to induce M2 macrophage polarization via the CSF-1/JAK2/STAT3 pathway, thereby contributing to chemoresistance within the tumor microenvironment. The expression of MELK in GC tissues from neoadjuvant chemotherapy patients correlated positively with CSF-1 and CD206. Moreover, patients with higher expression levels of MELK, CSF-1, or CD206 exhibited significantly shorter OS and DFS rates.
Conclusions: Our investigation underscores the critical role of MELK in promoting chemoresistance and inducing M2 macrophage polarization in GC. It proposes novel targets and methods for the treatment of GC, as well as prognostic factors for neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Keywords: Chemoresistance; Gastric cancer; MELK; Polarization; Prognosis; Tumor-associated macrophages.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

