Detecting heart stress using NT-proBNP in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension or high-normal blood pressure: a cross-sectional multicentric study
- PMID: 39135091
- PMCID: PMC11321074
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-024-02391-z
Detecting heart stress using NT-proBNP in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension or high-normal blood pressure: a cross-sectional multicentric study
Abstract
Background: We evaluated the prevalence of "heart stress" (HS) based on NT-proBNP cut-points proposed by the 2023 Consensus of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) in asymptomatic patients with T2DM and hypertension or high-normal blood pressure (BP) eligible for SGLT2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) and/or GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP1-RA), drugs with proven benefits on reducing the incidence of HF, hospitalizations, cardiovascular events and mortality.
Methods: A cross-sectional multicentric study was conducted on 192 consecutive outpatients, aged ≥ 55 years, with hypertension or high-normal BP, referred to three diabetology units. NT-proBNP was collected before starting new anti-diabetic therapy. Patients with known HF were excluded, and participants were classified based on the age-adjusted NT-proBNP cut-points.
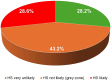
Results: Mean age: 70.3 ± 7.8 years (67.5% males). Patients with obesity (BMI ≥ 30 Kg/m2): 63.8%. Median NT-proBNP: 96.0 (38.8-213.0) pg/mL. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD, eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73m2): 32.1%. Mean arterial BP: 138.5/77.0 ± 15.8/9.9 mmHg. The NT-proBNP values, according to the proposed age-adjusted cut-points, classified 28.6% of patients as "HS likely" (organize elective echocardiography and specialist evaluation), 43.2% as "HS not likely" (a grey area, repeat NT-proBNP at six months) and 28.2% as "very unlikely HS" (repeat NT-proBNP at one year). The presence of CKD and the number of anti-hypertensive drugs, but not glycemic parameters, were independently associated with HS.
Conclusions: According to NT-proBNP, over a quarter of T2DM patients with hypertension/high-normal BP, among those eligible for SGLT2i and/or GLP1-RA, were already at risk of cardiac damage, even subclinical. Most would receive an indication to echocardiogram and be referred to a specialist, allowing the early implementation of effective strategies to prevent or delay the progression to advanced stages of cardiac disease and overt HF.
Keywords: GLP1-RA; Heart stress; Hypertension; NT-proBNP; SGLT2i; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sattar N, Lee MMY, Kristensen SL, Branch KRH, Del Prato S, Khurmi NS, et al. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;9(10):653–62. 10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00203-5 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous