LncRNA-encoded peptides in cancer
- PMID: 39135098
- PMCID: PMC11320871
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-024-01591-0
LncRNA-encoded peptides in cancer
Abstract
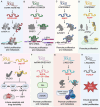
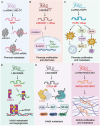
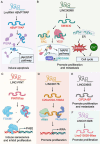
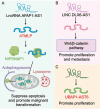
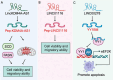
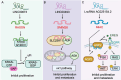
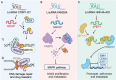
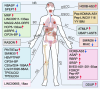
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), once considered transcriptional noise, have emerged as critical regulators of gene expression and key players in cancer biology. Recent breakthroughs have revealed that certain lncRNAs can encode small open reading frame (sORF)-derived peptides, which are now understood to contribute to the pathogenesis of various cancers. This review synthesizes current knowledge on the detection, functional roles, and clinical implications of lncRNA-encoded peptides in cancer. We discuss technological advancements in the detection and validation of sORFs, including ribosome profiling and mass spectrometry, which have facilitated the discovery of these peptides. The functional roles of lncRNA-encoded peptides in cancer processes such as gene transcription, translation regulation, signal transduction, and metabolic reprogramming are explored in various types of cancer. The clinical potential of these peptides is highlighted, with a focus on their utility as diagnostic biomarkers, prognostic indicators, and therapeutic targets. The challenges and future directions in translating these findings into clinical practice are also discussed, including the need for large-scale validation, development of sensitive detection methods, and optimization of peptide stability and delivery.
Keywords: Application; Cancer; Long non-coding RNA; Peptide; Small open reading frame.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

