The biological applications of near-infrared optical nanomaterials in atherosclerosis
- PMID: 39135099
- PMCID: PMC11320980
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-024-02703-1
The biological applications of near-infrared optical nanomaterials in atherosclerosis
Abstract
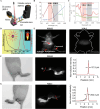
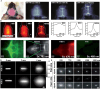
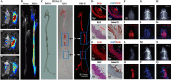
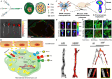
Purpose of review: Atherosclerosis, a highly pathogenic and lethal disease, is difficult to locate accurately via conventional imaging because of its scattered and deep lesions. However, second near-infrared (NIR-II) nanomaterials show great application potential in the tracing of atherosclerotic plaques due to their excellent penetration and angiographic capabilities.
Recent findings: With the development of nanotechnology, among many nanomaterials available for the visual diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, optical nanomaterials provide strong support for various biomedical applications because of their advantages, such as noninvasive, nondestructive and molecular component imaging. Among optical nanomaterials of different wavelengths, NIR-II-range (900 ~ 1700 nm) nanomaterials have been gradually applied in the visual diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis and other vascular diseases because of their deep biological tissue penetration and limited background interference. This review explored in detail the prospects and challenges of the biological imaging and clinical application of NIR-II nanomaterials in treating atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Cardiovascular disease; Macrophage polarization; NIR-II nanoparticle; NIRF.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Organization GWH. World health statistics 2022: monitoring health for the SDGs, sustainable development goals. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022.
-
- Shen L, Li H, Chen W, Su Y, Yu J, Chen M, Shu G, Qiao E, Guo X, Xu M, et al. Integrated application of transcriptome and metabolomics reveals potential therapeutic targets for the polarization of atherosclerotic macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022;1868: 166550. 10.1016/j.bbadis.2022.166550. 10.1016/j.bbadis.2022.166550 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2023M741498/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- LSSY24H020006/Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province
- LSSY24H020006/Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province
- 2024KY560/Medical Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Province
- 2022ZDYF12/Key Research and Development Program of Lishui
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

