Systemic immunoinflammatory indexes in albuminuric adults are negatively associated with α-klotho: evidence from NHANES 2007-2016
- PMID: 39135529
- PMCID: PMC11328598
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2385059
Systemic immunoinflammatory indexes in albuminuric adults are negatively associated with α-klotho: evidence from NHANES 2007-2016
Abstract
Background: Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) is a novel inflammatory biomarker closely associated with the inflammatory response and chronic kidney disease. Klotho is implicated as a pathogenic factor in the progression of kidney disease, and supplementation of Klotho may delay the progression of chronic kidney disease by inhibiting the inflammatory response. Our aim is to investigate the potential relationship between SII and Klotho in adult patients in the United States and explore the differences in the populations with and without albuminuria.
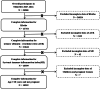
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study recruiting adult participants with complete data on SII, Klotho, and urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2007 to 2016. SII was calculated as platelet count × neutrophil count/lymphocyte count, with abnormal elevation defined as values exceeding 330 × 10^9/L. Albuminuria was defined as ACR >30 mg/g. Weighted multivariable regression analysis and subgroup analysis were employed to explore the independent relationship between SII and Klotho.
Results: Our study included a total of 10,592 individuals. In all populations, non-albuminuria population, and proteinuria population with ACR ≥ 30, participants with abnormally elevated SII levels, as compared to those with SII less than 330 × 10^9/L, showed a negative correlation between elevated SII levels and increased Klotho, which persisted after adjusting for covariates.
Conclusions: There is a negative correlation between SII and Klotho in adult patients in the United States. This finding complements previous research but requires further analysis through large prospective studies.
Keywords: NHANES; Systemic immune-inflammation index; albuminuria adults; cross-sectional study; α-Klotho.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources