Effects of Portulaca oleracea (purslane) on liver function tests, metabolic profile, oxidative stress and inflammatory biomarkers in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial
- PMID: 39135554
- PMCID: PMC11317426
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1371137
Effects of Portulaca oleracea (purslane) on liver function tests, metabolic profile, oxidative stress and inflammatory biomarkers in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a prevalent chronic liver disease. Portulaca oleracea exhibits anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective effects. This clinical trial aimed to investigate the potential benefits of Portulaca oleracea in improving NAFLD.
Methods: This double-blind, randomized clinical trial enrolled 70 patients with NAFLD assigned to either the intervention group (n = 35) or placebo group (n = 35) using stratified block randomization. The intervention group received 700 mg Portulaca oleracea supplement for eight weeks, while the control group received placebo capsules. In addition, all participants received a calorie-restricted diet. Liver steatosis and fibrosis were assessed using elastography along with liver function and metabolic tests, blood pressure measurements, body composition analysis and dietary records pre-and post-intervention.
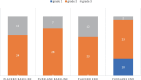
Results: The average age of the participants was 44.01 ± 8.6 years, of which 34 (48.6%) were women. The group receiving Portulaca oleracea showed significant weight changes, body mass index, fat mass index, and waist circumference compared to the placebo (p < 0.001). In addition, blood sugar, lipid profile, liver enzymes aspartate and alanine transaminase, gamma-glutamyl transferase, and systolic blood pressure were significantly improved in the intervention group compared to those in the placebo (p < 0.05). During the study, inflammatory and oxidative stress indicators, improved significantly (p < 0.05). Based on the elastography results, the hepatorenal ultrasound index and liver stiffness decreased significantly in the Portulaca oleracea group compared to the placebo (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The present clinical trial showed that receiving Portulaca oleracea supplement for eight weeks can improve the condition of liver steatosis and fibrosis in patients with NAFLD.
Keywords: Portulaca oleracea; inflammation; liver steatosis; non-alcoholic fatty liver; oxidative stress; purslane.
Copyright © 2024 Milkarizi, Barghchi, Belyani, Bahari, Rajabzade, Ostad, Goshayeshi, Nematy and Askari.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of Portulaca Oleracea (purslane) extract on liver enzymes, lipid profile, and glycemic status in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, double-blind clinical trial.Phytother Res. 2021 Jun;35(6):3145-3156. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6972. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Phytother Res. 2021. PMID: 33880813 Clinical Trial.
-
The clinical effects of purslane (Portulaca oleracea) seeds on metabolic profiles in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled clinical trial.Phytother Res. 2019 May;33(5):1501-1509. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6342. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Phytother Res. 2019. PMID: 30895694 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of purslane (Portulaca oleracea) for mild to moderate chronic hand eczema; A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.Explore (NY). 2024 May-Jun;20(3):401-410. doi: 10.1016/j.explore.2023.10.005. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Explore (NY). 2024. PMID: 37872023 Clinical Trial.
-
Ameliorative effects of Portulaca oleracea L. (purslane) on the metabolic syndrome: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Dec 5;299:115672. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115672. Epub 2022 Sep 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36064150 Review.
-
The therapeutic effects of Portulaca oleracea L. in hepatogastric disorders.Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Feb;42(2):127-132. doi: 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2018.07.016. Epub 2018 Oct 13. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30327154 Review. English, Spanish.
References
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO) . EASL-EASD-EASO clinical practice guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Obes Facts. (2016) 9:65–90. doi: 10.1159/000443344, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources