Progress and trends in myocardial infarction-related long non-coding RNAs: a bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 39135912
- PMCID: PMC11317247
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1382772
Progress and trends in myocardial infarction-related long non-coding RNAs: a bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: Myocardial infarction (MI), a critical condition, substantially affects patient outcomes and mortality rates. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play a critical role in the onset and progression of MI. This study aimed to explore the related research on MI-related lncRNAs from a bibliometric perspective, providing new clues and directions for researchers in the field.
Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted on 7 August 2023, using the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) database to compile a dataset of all English-language scientific journals. The search gathered all relevant publications from January 2000 to August 2023 that pertain to MI-related lncRNAs. Data on countries, institutions, journals, authors, and keywords were collected, sorted, statistically analyzed, and visualized using CiteSpace 6.2.R4, VOSviewer 1.6.19, an online bibliometric analysis platform (http://bibliometric.com), and the bibliometric package in R-Studio 4.3.1. Articles were screened by two independent reviewers.
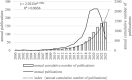
Results: Between January 2000 and August 2023, a total of 1,452 papers were published in the research field of MI-related lncRNAs. The year with the most publications was 2020, accounting for 256 papers. The publication volume displayed an exponential growth trend, fitting the equation y = 2.0215e0.2786x, R^2 = 0.97. In this domain, China leads in both the number of published papers (N = 1,034) and total citations, followed by the United States, Germany, Iran, and Italy. The most productive institution is Harbin Medical University (N = 144). The European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences had the highest number of publications (N = 46), while Circulation Research had the most citations (TC = 4,537), indicating its irreplaceable standing in this field. Research mainly focuses on the cardiovascular system, cellular biology, physiology, etc. The most productive author is Zhang Y. Apart from "Myocardial Infarction" and "LncRNA," the most frequent keywords include "expression," "atherosclerosis," and "apoptosis." Cluster analysis suggests current research themes concentrate on cardiovascular diseases and gene expression, cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury and protection, expression and proliferation, atherosclerosis and inflammatory response, among others. Keyword bursts indicate recent hot topics as targeting, autophagy, etc.
Conclusion: This bibliometric analysis reveals that research on MI-related lncRNAs has rapidly expanded between January 2000 and August 2023, primarily led by China and the United States. Our study highlights the significant biological roles of lncRNAs in the pathogenesis and progression of MI, including their involvement in gene expression regulation, atherosclerosis development, and apoptosis. These findings underscore the potential of lncRNAs as therapeutic targets and biomarkers for MI. Additionally, our study provides insights into the features and quality of related publications, as well as the future directions in this research field. There is a long road ahead, highlighting the urgent need for enhanced global academic exchange.
Keywords: bibliometric; cluster analysis; long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs); myocardial infarction (MI); web of science core collection.
Copyright © 2024 Meng, Tan, Wang and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Aria M., Cuccurullo C. (2017). bibliometrix: an R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Inf. 11 (4), 959–975. 10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007 - DOI
-
- Author Anonymous (2021). Group: summary of China cardiovascular health and disease report 2019. Chin. J. Geriatric Dis. Res. 7 (4), 4–15. 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-8757.2020.04.002 - DOI
-
- Bell R. D., Long X., Lin M., Bergmann J. H., Nanda V., Cowan S. L., et al. (2014). Identification and initial functional characterization of a human vascular cell–enriched long noncoding RNA. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, Vasc. Biol. 34 (6), 1249–1259. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303240 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

