Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals that MYBL2 in malignant epithelial cells is involved in the development and progression of ovarian cancer
- PMID: 39136009
- PMCID: PMC11317301
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1438198
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals that MYBL2 in malignant epithelial cells is involved in the development and progression of ovarian cancer
Abstract
Background: Ovarian carcinoma (OC) is a prevalent gynecological malignancy associated with high recurrence rates and mortality, often diagnosed at advanced stages. Despite advances in immunotherapy, immune exhaustion remains a significant challenge in achieving optimal tumor control. However, the exploration of intratumoral heterogeneity of malignant epithelial cells and the ovarian cancer tumor microenvironment is still limited, hindering our comprehensive understanding of the disease.
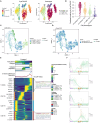
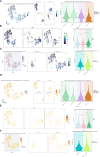
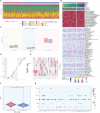
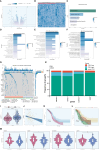
Materials and methods: Utilizing single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), we comprehensively investigated the cellular composition across six ovarian cancer patients with omental metastasis. Our focus centered on analysis of the malignant epithelial cells. Employing CytoTRACE and slingshot pseudotime analyses, we identified critical subpopulations and explored associated transcription factors (TFs) influencing ovarian cancer progression. Furthermore, by integrating clinical factors from a large cohort of bulk RNA sequencing data, we have established a novel prognostic model to investigate the impact of the tumor immune microenvironment on ovarian cancer patients. Furthermore, we have investigated the condition of immunological exhaustion.
Results: Our study identified a distinct and highly proliferative subgroup of malignant epithelial cells, known as C2 TOP2A+ TCs. This subgroup primarily consisted of patients who hadn't received neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ovarian cancer patients with elevated TOP2A expression exhibited heightened sensitivity to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT). Moreover, the transcription factor MYBL2 in this subgroup played a critical role in ovarian cancer development. Additionally, we developed an independent prognostic indicator, the TOP2A TCs Risk Score (TTRS), which revealed a correlation between the High TTRS Group and unfavorable outcomes. Furthermore, immune infiltration and drug sensitivity analyses demonstrated increased responsiveness to Paclitaxel, Cisplatin, and Gemcitabine in the Low TTRS Group.
Conclusion: This research deepens our understanding of malignant epithelial cells in ovarian cancer and enhances our knowledge of the ovarian cancer immune microenvironment and immune exhaustion. We have revealed the heightened susceptibility of the C2 TOP2A+ TCs subgroup to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and emphasized the role of MYBL2 within the C2 subgroup in promoting the occurrence and progression of ovarian cancer. These insights provide valuable guidance for the management of ovarian cancer treatment.
Keywords: epithelial cells; immune microenvironment; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; omentum; ovarian cancer; single-cell RNA sequencing.
Copyright © 2024 Shao, Lin, Xiahou, Zhao, Xu, Liu and Cai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Matulonis UA, Lorusso D, Oaknin A, Pignata S, Dean A, Denys H, et al. Efficacy and safety of mirvetuximab soravtansine in patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer with high folate receptor alpha expression: results from the SORAYA study. J Clin Oncol. (2023) 41:2436–45. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.01900 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

