Clinical, genomic and immune microenvironmental determinants of nivolumab response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 39136017
- PMCID: PMC11317249
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1390873
Clinical, genomic and immune microenvironmental determinants of nivolumab response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: In view of improving biomarkers predicting the efficacy of immunotherapy for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (R/M HNSCC), this multicenter retrospective study aimed to identify clinical, tumor microenvironmental, and genomic factors that are related to therapeutic response to the anti- Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) antibody, nivolumab, in patients with R/M HNSCC.
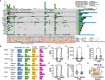
Methods: The study compared 53 responders and 47 non-responders, analyzing formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples using 14-marker multiplex immunohistochemistry and targeted gene sequencing.
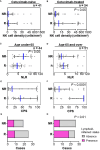
Results: Of 100 patients included, responders had significantly lower smoking and alcohol index, higher incidence of immune related adverse events, and higher PD-1 ligand (PD-L1) expression in immune cells as well as PD-L1 combined positive score (CPS) than non-responders. The frequency of natural killer cells was associated with nivolumab response in patients with prior cetuximab use, but not in cetuximab-naïve status. Age-stratified analysis showed nivolumab response was linked to high CPS and lymphoid-inflamed profiles in patients aged ≥ 65. In contrast, lower NLR in peripheral blood counts was associated with response in patients aged < 65. Notably, TP53 mutation-positive group had lower CPS and T cell densities, suggesting an immune-excluded microenvironment. Patients with altered tumor suppressor gene pathways, including TP53, CDKN2A, and SMAD4 mutations, had lower CPS, higher smoking index, and were associated with poor responses.
Conclusion: Nivolumab treatment efficacy in HNSCC is influenced by a combination of clinical factors, age, prior treatment, immune environmental characteristics, and gene mutation profiles.
Keywords: biomarker; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; immune profile; mutation; nivolumab.
Copyright © 2024 Tsujikawa, Ohno, Morita, Saburi, Mitsuda, Yoshimura, Kimura, Morimoto, Ogi, Shibata, Akashi, Kurata, Imoto, Shimizu, Kano, Watanabe, Yamazaki, Asada, Hayashi, Saito, Ozawa, Tsukahara, Oridate, Sano, Horii, Ueki, Maruo, Mukoyama, Hanai, Fukusumi, Iwai, Fujisawa, Fujii, Nibu, Iwae, Ueda, Chikuie, Yasumatsu, Matsuo, Umeno, Ono, Masuda, Toh, Itoh, Hirano and Asakage.
Conflict of interest statement
TT received lecture honoraria, consulting fees, and grants from Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and lecture honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, and Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. KO received grants from Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. HO and SS were employed by SCREEN Holdings Co., Ltd. YaS received lecture honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp, and Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. RH received lecture honoraria from Rakuten Medical Inc. YuS received grants from Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. KT received lecture honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp, and Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. NO received lecture honoraria and grants from Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd and lecture honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb. NH received lecture honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, and Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. KN received lecture honoraria from Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp, and Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. SI received lecture honoraria and grants from Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd and lecture honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb. KI received grants from SCREEN Holdings Co., Ltd. TAs received grants from Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
-
- Chow LQM, Haddad R, Gupta S, Mahipal A, Mehra R, Tahara M, et al. . Antitumor activity of pembrolizumab in biomarker-unselected patients with recurrent and/or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: results from the phase Ib KEYNOTE-012 expansion cohort. J Clin Oncol. (2016) 34:3838. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.68.1478 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Badoual C, Hans S, Merillon N, Van Ryswick C, Ravel P, Benhamouda N, et al. . PD-1–expressing tumor-infiltrating T cells are a favorable prognostic biomarker in HPV-associated head and neck cancerPD-1–expressing T cells in HPV-associated oral cancers. Cancer Res. (2013) 73:128–38. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2606 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

