Liver fibrosis stage based on the four factors (FIB-4) score or Forns index in adults with chronic hepatitis C
- PMID: 39136280
- PMCID: PMC11320661
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011929.pub2
Liver fibrosis stage based on the four factors (FIB-4) score or Forns index in adults with chronic hepatitis C
Abstract
Background: The presence and severity of liver fibrosis are important prognostic variables when evaluating people with chronic hepatitis C (CHC). Although liver biopsy remains the reference standard, non-invasive serological markers, such as the four factors (FIB-4) score and the Forns index, can also be used to stage liver fibrosis.
Objectives: To determine the diagnostic accuracy of the FIB-4 score and Forns index in staging liver fibrosis in people with chronic hepatitis C (CHC) virus, using liver biopsy as the reference standard (primary objective). To compare the diagnostic accuracy of these tests for staging liver fibrosis in people with CHC and explore potential sources of heterogeneity (secondary objectives).
Search methods: We used standard Cochrane search methods for diagnostic accuracy studies (search date: 13 April 2022).
Selection criteria: We included diagnostic cross-sectional or case-control studies that evaluated the performance of the FIB-4 score, the Forns index, or both, against liver biopsy, in the assessment of liver fibrosis in participants with CHC. We imposed no language restrictions. We excluded studies in which: participants had causes of liver disease besides CHC; participants had successfully been treated for CHC; or the interval between the index test and liver biopsy exceeded six months.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted data. We performed meta-analyses using the bivariate model and calculated summary estimates. We evaluated the performance of both tests for three target conditions: significant fibrosis or worse (METAVIR stage ≥ F2); severe fibrosis or worse (METAVIR stage ≥ F3); and cirrhosis (METAVIR stage F4). We restricted the meta-analysis to studies reporting cut-offs in a specified range (+/-0.15 for FIB-4; +/-0.3 for Forns index) around the original validated cut-offs (1.45 and 3.25 for FIB-4; 4.2 and 6.9 for Forns index). We calculated the percentage of people who would receive an indeterminate result (i.e. above the rule-out threshold but below the rule-in threshold) for each index test/cut-off/target condition combination.
Main results: We included 84 studies (with a total of 107,583 participants) from 28 countries, published between 2002 and 2021, in the qualitative synthesis. Of the 84 studies, 82 (98%) were cross-sectional diagnostic accuracy studies with cohort-based sampling, and the remaining two (2%) were case-control studies. All studies were conducted in referral centres. Our main meta-analysis included 62 studies (100,605 participants). Overall, two studies (2%) had low risk of bias, 23 studies (27%) had unclear risk of bias, and 59 studies (73%) had high risk of bias. We judged 13 studies (15%) to have applicability concerns regarding participant selection. FIB-4 score The FIB-4 score's low cut-off (1.45) is designed to rule out people with at least severe fibrosis (≥ F3). Thirty-nine study cohorts (86,907 participants) yielded a summary sensitivity of 81.1% (95% confidence interval (CI) 75.6% to 85.6%), specificity of 62.3% (95% CI 57.4% to 66.9%), and negative likelihood ratio (LR-) of 0.30 (95% CI 0.24 to 0.38). The FIB-4 score's high cut-off (3.25) is designed to rule in people with at least severe fibrosis (≥ F3). Twenty-four study cohorts (81,350 participants) yielded a summary sensitivity of 41.4% (95% CI 33.0% to 50.4%), specificity of 92.6% (95% CI 89.5% to 94.9%), and positive likelihood ratio (LR+) of 5.6 (95% CI 4.4 to 7.1). Using the FIB-4 score to assess severe fibrosis and applying both cut-offs together, 30.9% of people would obtain an indeterminate result, requiring further investigations. We report the summary accuracy estimates for the FIB-4 score when used for assessing significant fibrosis (≥ F2) and cirrhosis (F4) in the main review text. Forns index The Forns index's low cut-off (4.2) is designed to rule out people with at least significant fibrosis (≥ F2). Seventeen study cohorts (4354 participants) yielded a summary sensitivity of 84.7% (95% CI 77.9% to 89.7%), specificity of 47.9% (95% CI 38.6% to 57.3%), and LR- of 0.32 (95% CI 0.25 to 0.41). The Forns index's high cut-off (6.9) is designed to rule in people with at least significant fibrosis (≥ F2). Twelve study cohorts (3245 participants) yielded a summary sensitivity of 34.1% (95% CI 26.4% to 42.8%), specificity of 97.3% (95% CI 92.9% to 99.0%), and LR+ of 12.5 (95% CI 5.7 to 27.2). Using the Forns index to assess significant fibrosis and applying both cut-offs together, 44.8% of people would obtain an indeterminate result, requiring further investigations. We report the summary accuracy estimates for the Forns index when used for assessing severe fibrosis (≥ F3) and cirrhosis (F4) in the main text. Comparing FIB-4 to Forns index There were insufficient studies to meta-analyse the performance of the Forns index for diagnosing severe fibrosis and cirrhosis. Therefore, comparisons of the two tests' performance were not possible for these target conditions. For diagnosing significant fibrosis and worse, there were no significant differences in their performance when using the high cut-off. The Forns index performed slightly better than FIB-4 when using the low/rule-out cut-off (relative sensitivity 1.12, 95% CI 1.00 to 1.25; P = 0.0573; relative specificity 0.69, 95% CI 0.57 to 0.84; P = 0.002).
Authors' conclusions: Both the FIB-4 score and the Forns index may be considered for the initial assessment of people with CHC. The FIB-4 score's low cut-off (1.45) can be used to rule out people with at least severe fibrosis (≥ F3) and cirrhosis (F4). The Forns index's high cut-off (6.9) can be used to diagnose people with at least significant fibrosis (≥ F2). We judged most of the included studies to be at unclear or high risk of bias. The overall quality of the body of evidence was low or very low, and more high-quality studies are needed. Our review only captured data from referral centres. Therefore, when generalising our results to a primary care population, the probability of false positives will likely be higher and false negatives will likely be lower. More research is needed in sub-Saharan Africa, since these tests may be of value in such resource-poor settings.
Copyright © 2024 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest to declare
Figures
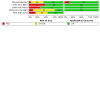

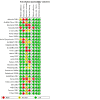
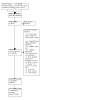
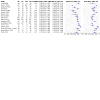
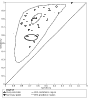
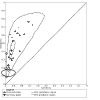
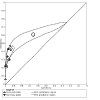

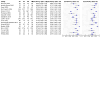
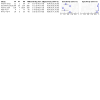
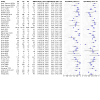



Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Abdel‐Hameed 2021a {published and unpublished data}
Abdel‐Hameed 2021b {published and unpublished data}
Abdelsameea 2020 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Abdelsameea E, Alsebaey A, Abdel-Razek W, Ehsan N, Morad W, Salama M, et al. Elastography and serum markers of fibrosis versus liver biopsy in 1270 Egyptian patients with hepatitis C. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2020;32(12):1553-8. [DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001672] - DOI - PubMed
Abo El‐Khair 2019 {published data only}
-
- Abo El-Khair SM, El-Alfy HA, Elsamanoudy AZ, Elhammady D, Abd-Elfattah N, Eldeek B, et al. Development of a novel glycated protein-based fibrosis prediction score for determination of significant liver fibrosis in HCV-infected patients, a preliminary study. Journal of Medical Virology 2019;92(12):3525-33. [DOI: 10.1002/jmv.26204] - DOI - PubMed
Ahmad 2011 {published data only}
Alboraie 2015 {published data only}
-
- Alboraie M, Khairy M, Elsharkawy M, Asem N, Elsharkawy A, Esmat G. Value of Egy-Score in diagnosis of significant, advanced hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis compared to aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index, FIB-4 and Forns' index in chronic hepatitis C virus. Hepatology Research 2015;45(5):560-70. [DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12385] - DOI - PubMed
Amorim 2012 {published data only}
-
- Amorim TG, Staub GJ, Lazzarotto C, Silva AP, Manes J, Ferronato Mda G, et al. Validation and comparison of simple noninvasive models for the prediction of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Annals of Hepatology 2012;11(6):855-61. - PubMed
Andrés‐Otero 2016 {published data only}
-
- Andrés-Otero MJ, De-Blas-Giral I, Puente-Lanzarote JJ, Serrano-Aulló T, Morandeira MJ, Lorente S, et al. Multiple approaches to assess fourteen non-invasive serum indexes for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C patients. Clinical Biochemistry 2016;49(7-8):560-5. [DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2015.12.017] - DOI - PubMed
Attallah 2012 {published data only}
-
- Attallah AM, Omran MM, Farid K, El-Bendary M, Emran TM, Albannan MS, et al. Development of a novel score for liver fibrosis staging and comparison with eight simple laboratory scores in large numbers of HCV-monoinfected patients. Clinica Chimica Acta 2012;413(21-22):1725-30. [DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2012.06.031] - DOI - PubMed
Baldwin 2020 {published data only}
-
- Baldwin N, Ravi S, Boudreaux J, Lin CP, Orandi B, Gray M. NALFD fibrosis score outperforms FIB-4 and Apri in predicting advanced fibrosis in non-NAFLD etiologies of liver disease. Gastroenterology 2020;158:1384-5. [0016-5085 1528-0012]
Bonnard 2015 {published data only}
-
- Bonnard P, Elsharkawy A, Zalata K, Delarocque‐Astagneau E, Biard L, Le Fouler L, et al. Comparison of liver biopsy and noninvasive techniques for liver fibrosis assessment in patients infected with HCV‐genotype 4 in Egypt. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 2015;22(3):245-53. [DOI: 10.1111/jvh.12285] - DOI - PubMed
Bourliere 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bourliere M, Penaranda G, Renou C, Botta‐Fridlund D, Tran A, Portal I, et al. Validation and comparison of indexes for fibrosis and cirrhosis prediction in chronic hepatitis C patients: proposal for a pragmatic approach classification without liver biopsies. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 2006;3(10):659-70. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2006.00736.x] - DOI - PubMed
Calès 2010 {published data only}
Cheng 2019 {published data only}
-
- Cheng CH, Chu CY, Chen HL, Lin IT, Wu CH, Lee YK, et al. Subgroup analysis of the predictive ability of aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index (APRI) and fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) for assessing hepatic fibrosis among patients with chronic hepatitis C. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology & Infection 2019;53(4):542-9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jmii.2019.09.002] - DOI - PubMed
Conti 2019 {published data only}
Cordie 2018 {published data only}
Corradi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Corradi F, Piscaglia F, Flori S, D’Errico-Grigioni A, Vasuri F, Tame MR, et al. Assessment of liver fibrosis in transplant recipients with recurrent HCV infection: usefulness of transient elastography. Digestive and Liver Disease 2009;41(3):217-25. - PubMed
Crisan 2012 {published data only}
-
- Crisan D, Radu C, Lupsor M, Sparchez Z, Grigorescu MD, Grigorescu M. Two or more synchronous combination of noninvasive tests to increase accuracy of liver fibrosis assessement in chronic hepatitis C; results from a cohort of 446 patients. Hepatitis monthly 2012;12(3):177. [DOI: 10.5812/hepatmon.853] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Demma 2018 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Demma S, Benmassaoud A, Campbell S, Macdonald D. An evaluation of Elift, Fib-4 and APRI for exclusion of advanced fibrosis in a real-world Hepatitis C treatment cohort. Hepatology 2018;68(Suppl 1):910A-1A.
De Oliveira 2016 {published data only}
Ferenci 2014 {published and unpublished data}
Fontaine 2009 {published data only}
-
- Fontaine H, Nalpas B, Vallet-Pichard A, Mallet V, Pol S. Low diagnosis accuracy of fibrotest and FIB-4 in HCV-infected haemodialysis and kidney recipients. Hepatology 2009;50(Suppl 4):1064A.
Forns 2002a {published data only}
Forns 2002b {published data only}
Fouad 2018 {published data only}
-
- Fouad R, Elbaz T, Abdel Alem S, Elsharkawy A, Negm M, Khairy M, et al. Evaluation of accuracy of elastography point quantification versus other noninvasive modalities in staging of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C virus patients. European Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2018;30:882-7. - PubMed
Fujita 2018 {published data only}
Gamil 2017 {published data only}
-
- Gamil M, Alboraie M, El-Sayed M, Elsharkawy A, Asem N, Elbaz T, et al. Novel scores combining AFP with non-invasive markers for prediction of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C patients. Journal of Medical Virology 2017;90(6):1080-6. - PubMed
Gökan 2016 {published data only}
Gorka‐Dynysiewicz 2019 {published data only}
Gorka‐Dynysiewicz 2020 {published data only}
-
- Gorka-Dynysiewicz J, Pazgan-Simon M, Zuwala-Jagiello J. Accurate prediction of significant liver fibrosis using the Pentra score model in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Polish Archives Of Internal Medicine 2020;130(2):112-20. - PubMed
Gounder 2018 {published data only}
-
- Gounder PP, Haering C, Bruden DJ, Townshend-Bulson L, Simons BC, Spradling PR, et al. Does incorporating change in APRI or FIB-4 indices over time improve the accuracy of a single index for identifying liver fibrosis in persons with chronic hepatitis C virus infection? Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 2018;52(1):60-6. [DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000753] - DOI - PubMed
Guilabert 2010 {published data only}
-
- Guilabert MI, Mena-Bernal CH, Pozo González J, Pozo Pérez MA. Retrospective diagnostic accuracy study of liver fibrosis of Fibroscan, APRI, FIB-4 and Forns compared to biopsy in HCV patients both with and without co-infection of HIV [Estudio retrospectivo de la capacidad de evaluación de fibrosis hepática del FibroScan®, APRI, FIB-4 y FORNS con referencia a la biopsia hepática de pacientes con hepatitis crónica C, mono y coinfectados con VIH]. Gastroenterología y Hepatología 2010;33(6):425-32. [DOI: 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2010.02.005] - DOI - PubMed
Güzelbulut 2011 {published data only}
-
- Güzelbulut F, Akkan Cetinkya Z, Sezikli M, Yaşar B, Özkara S, Kurdaş Övünç AO. AST-platelet ratio index, Forns index and FIB-4 in the prediction of significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C [Kronik hepatit C’li hastalarda belirgin fibrozis ve sirozun belirlenmesinde AST-platelet oran› indeksi, Forns indeksi ve FIB-4’ün yeri]. Turkish Journal of Gastroenterolgy 2011;22(3):279-85. [DOI: 10.4318/tjg.2011.0213] - DOI - PubMed
Hashem 2021 {published data only}
Holmberg 2013 {published data only}
Hseih 2012 {published data only}
Hsu 2019 {published and unpublished data}
Iacobellis 2005 {published data only}
Ikatura 2021 {published and unpublished data}
Kamphues 2010 {published data only}
Kitajima 2016 {published data only}
-
- Kitajima T, Kaido T, Hamaguchi Y, Yagi S, Taura K, Fujimoto Y, et al. Validation of the FIB‐4 index for evaluation of fibrosis in patients with recurrent hepatitis C after living donor liver transplantation: a single center experience. Hepatology Research 2016;46(8):752-7. [DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12617] - DOI - PubMed
Koller 2014 {published data only}
Ladero 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ladero JM, Delkader J, Ortega L, Fernández C, Devesa MJ, López-Alonso G, et al. Non-invasive evaluation of the fibrosis stage in chronic hepatitis C: a comparative analysis of nine scoring methods. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 2010;45(1):51-9. [DOI: 10.3109/00365520903305544] - DOI - PubMed
Leroy 2007 {published data only}
Loko 2008 {published data only}
-
- Loko MA, Castera L, Dabis F, Le Bail B, Winnock M, Coureau G, et al, Groupe d'Epidémiologie Clinique du SIDA en Aquitaine. Validation and comparison of simple noninvasive indexes for predicting liver fibrosis in HIV-HCV-coinfected patients: ANRS CO3 Aquitaine cohort. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2008;103(8):1973-80. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2008.01954.x] - DOI - PubMed
Macías 2006 {published data only}
Maheshwari 2013 {published data only}
-
- Maheshwari R, Yang J, Miller L. FIB-4 Index as a non-invasive and inexpensive predictor of hepatic fibrosis in a primarily uninsured African-American population with chronic hepatitis C. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2013;108(Suppl 1):S112. [DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2013.265] - DOI
Martinez 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Martinez SM, Fernández‐Varo G, González P, Sampson E, Bruguera M, Navasa M, et al. Assessment of liver fibrosis before and after antiviral therapy by different serum marker panels in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2011;33(1):138-48. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2010.04500.x] - DOI - PubMed
Matsuura 2018 {published data only}
Mossong 2011 {published data only}
-
- Mossong J, Bill S, Hawotte K, Gilson G, Knolle U, Weber J, et al. Predicting significant fibrosis in hepatitis C patients in Luxembourg using serological markers. Bulletin de la Société des Sciences Médicales du Grand-Duché de Luxembourg 2011;1:19-30. - PubMed
Nan 2019 {published data only}
Omran 2018 {published data only}
Ozel 2015 {published data only}
Paranaguá‐Vezozzo 2017 {published data only}
Patel 2017 {published data only}
-
- Patel R, Rassameehiran S, Patil R, Dhingra S, Sood GK. Diagnostic utility of non-invasive markers for staging of liver disease in hepatitis C patients with ESRD on haemodialysis. Gastroenterology 2017;152(5):S1165-6.
Portilla 2009 {published data only}
-
- Portilla J, López-Burgos A, Saiz-De-La-Hoya-Zamácola P, Sánchez-Payá J, Bedía-Collantes M, Faraco-Atienzar I, et al. Utility of 2 predictive biochemical models of hepatic fibrosis grade in the prison population with hepatitis C [Utilidad de 2 modelos bioquímicos predictivos del grado de fibrosis hepática en la población penitenciaria con hepatitis C]. Gastroenterología y Hepatología 2009;32(6):387-94. [DOI: 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2009.01.176] - DOI - PubMed
Qian 2019 {published data only}
-
- Qian X, Zheng S, Wang L, Yao M, Guan G, Wen X, et al. Exploring the diagnostic potential of serum golgi protein 73 for hepatic necroinflammation and fibrosis in chronic HCV infection with different stages of liver injuries. Disease Markers 2019;2019:3862024. [DOI: 10.1155/2019/3862024] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Ramzy 2021 {published data only}
-
- Ramzy I, Fouad R, Salama R, Abdellatif Z, Elsharkawy A, Zayed N, et al. Evaluation of red cell distribution width to platelet ratio as a novel non-invasive index for predicting hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Arab Journal of Gastroenterology 2021;22(1):6-11. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ajg.2020.12.003] - DOI - PubMed
Schmid 2015 {published data only}
-
- Schmid P, Bregenzer A, Huber M, Rauch A, Jochum W, Müllhaupt B, et al, Swiss HIV Cohort Study. Progression of liver fibrosis in HIV/HCV co-infection: a comparison between non-invasive assessment methods and liver biopsy. PLOS One 2015;10(9):e0138838. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138838] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Schmoyer 2020 {published data only}
Sebastiani 2008a {published data only}
Sebastiani 2008b {published data only}
Sebastiani 2012 {published data only}
Segovia 2008 {published data only}
-
- Segovia MC, Lyden ER, Bernard T, McCashland TM. Evaluation of FIB-4 as a marker of fibrosis in HCV infected patients who underwent liver transplantation. Hepatology 2008;48(4 Suppl):576A.
Sène 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sène D, Limal N, Messous D, Ghillani-Dalbin P, Charlotte F, Thiollière JM, et al. Biological markers of liver fibrosis and activity as non-invasive alternatives to liver biopsy in patients with chronic hepatitis C and associated mixed cryoglobulinemia vasculitis. Clinical Biochemistry 2006;39(7):715-21. [DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2006.04.019] - DOI - PubMed
Shaikh 2009 {published data only}
-
- Shaikh S, Memon MS, Ghani H, Baloch GH, Jaffery M, Shaikh K. Validation of three non-invasive markers in assessing the severity of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Journal of the College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan 2009;19(8):478-82. - PubMed
Shiha 2017 {published data only}
-
- Shiha G, Seif S, Eldesoky A, Elbasiony M, Soliman R, Metwally A, et al. A simple bedside blood test (Fibrofast; FIB-5) is superior to FIB-4 index for the differentiation between non-significant and significant fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology International 2017;11(3):286-91. [DOI: 10.1007/s12072-017-9796-z] - DOI - PubMed
Shiha 2022a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Shiha G, Soliman R, Mikhail NN, Alswat K, Abdo A, Sanai F, et al. Development and multicenter validation of FIB-6: a novel, machine learning, simple bedside score to rule out liver cirrhosis and compensated advanced chronic liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology Research 2022;52:165-75. [DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13729] - DOI - PubMed
Shiha 2022b {published and unpublished data}
-
- Shiha G, Soliman R, Mikhail NN, Alswat K, Abdo A, Sanai F, et al. Development and multicenter validation of FIB-6: A novel, machine learning, simple bedside score to rule out liver cirrhosis and compensated advanced chronic liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology Research 2022;52:165-75. [DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13729] - DOI - PubMed
Shiha 2022c {published and unpublished data}
-
- Shiha G, Soliman R, Mikhail NN, Alswat K, Abdo A, Sanai F, et al. Development and multicenter validation of FIB-6: A novel, machine learning, simple bedside score to rule out liver cirrhosis and compensated advanced chronic liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology Research 2022;52:165-75. [DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13729] - DOI - PubMed
Shiha 2022d {published and unpublished data}
-
- Shiha G, Soliman R, Mikhail NN, Alswat K, Abdo A, Sanai F, et al. Development and multicenter validation of FIB-6: A novel, machine learning, simple bedside score to rule out liver cirrhosis and compensated advanced chronic liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology Research 2022;52:165-75. [DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13729] - DOI - PubMed
Shiha 2022e {published and unpublished data}
-
- Shiha G, Soliman R, Mikhail NN, Alswat K, Abdo A, Sanai F, et al. Development and multicenter validation of FIB-6: A novel, machine learning, simple bedside score to rule out liver cirrhosis and compensated advanced chronic liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology Research 2022;52:165-75. [DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13729] - DOI - PubMed
Shiha 2022f {published and unpublished data}
-
- Shiha G, Soliman R, Mikhail NN, Alswat K, Abdo A, Sanai F, et al. Development and multicenter validation of FIB-6: A novel, machine learning, simple bedside score to rule out liver cirrhosis and compensated advanced chronic liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology Research 2022;52:165-75. [DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13729] - DOI - PubMed
Shiha 2022g {published and unpublished data}
-
- Shiha G, Soliman R, Mikhail NN, Alswat K, Abdo A, Sanai F, et al. Development and multicenter validation of FIB-6: A novel, machine learning, simple bedside score to rule out liver cirrhosis and compensated advanced chronic liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology Research 2022;52:165-75. [DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13729] - DOI - PubMed
Shiha 2022h {published and unpublished data}
-
- Shiha G, Soliman R, Mikhail NN, Alswat K, Abdo A, Sanai F, et al. Development and multicenter validation of FIB-6: A novel, machine learning, simple bedside score to rule out liver cirrhosis and compensated advanced chronic liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology Research 2022;52:165-75. [DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13729] - DOI - PubMed
Shiha 2022i {published and unpublished data}
-
- Shiha G, Soliman R, Mikhail NN, Alswat K, Abdo A, Sanai F, et al. Development and multicenter validation of FIB-6: A novel, machine learning, simple bedside score to rule out liver cirrhosis and compensated advanced chronic liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology Research 2022;52:165-75. [DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13729] - DOI - PubMed
Shiha 2022j {published and unpublished data}
-
- Shiha G, Soliman R, Mikhail NN, Alswat K, Abdo A, Sanai F, et al. Development and multicenter validation of FIB-6: A novel, machine learning, simple bedside score to rule out liver cirrhosis and compensated advanced chronic liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology Research 2022;52:165-75. [DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13729] - DOI - PubMed
Silva Junior 2014 {published data only}
Şirli 2010 {published data only}
Stauber 2015 {published data only}
-
- Stauber RE, Maieron A, Posch A, Pock H, Streit A, Lackner C. FIB-4, a simple fibrosis test, accurately predicts METAVIR F3/F4 stage in chronic hepatitis C. United European Gastroenterology Journal 2015;3(5S):A519.
Sterling 2006 {published and unpublished data}
Stibbe 2011 {published data only}
Tachi 2015 {published data only}
Tanwar 2017 {published data only}
Toson 2017 {published data only}
-
- Toson ES, Shiha GE, El-Mezayen HA, Samir W, El-Khininy MM. Noninvasive estimation of liver fibrosis in biopsy-proven hepatitis C virus-infected patients: angiogenic fibrogenic link. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2017;29(2):199-207. [DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000775] - DOI - PubMed
Trang 2008 {published data only}
Trifan 2009 {published data only}
-
- Trifan A, Cojocariu C, Sfarti C, Stanciu C. Prospective clinical trial on the accuracy of non-invasive tests to predict liver fibrosis in chronic HCV patients. Hepatology 2009;50(4 Suppl):1074A-5A.
Tsukano 2017 {published data only}
-
- Tsukano N, Miyase S, Saeki T, Mizobe K, Iwashita H, Arima N, et al. Usefulness of virtual touch quantification for staging liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C, and factors affecting liver stiffness measurement failure compared with liver biopsy. Hepatology Research 2018;48(5):373-82. [DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13041] - DOI - PubMed
Tural 2009 {published data only}
-
- Tural C, Tor J, Sanvisens A, Pérez–Alvarez N, Martínez E, Ojanguren I, et al. Accuracy of simple biochemical tests in identifying liver fibrosis in patients co-infected with human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2009;7(3):339-45. [DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2008.11.019] - DOI - PubMed
Udompap 2020 {published data only}
-
- Udompap P, Sukonrut K, Suvannarerg V, Pongpaibul A, Charatcharoenwitthaya P. Prospective comparison of transient elastography, point shear wave elastography, APRI and FIB-4 for staging liver fibrosis in chronic viral hepatitis. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 2020;27(4):437-48. [DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13246] - DOI - PubMed
Usluer 2012 {published data only}
Vallet‐Pichard 2007 {published data only}
Wang 2015 {published data only}
-
- Wang CC, Liu CH, Lin CL, Wang PC, Tseng TC, Lin HH, et al. Fibrosis index based on four factors better predicts advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis than aspartate aminotransferase/platelet ratio index in chronic hepatitis C patients. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association 2015;114(10):923-8. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jfma.2015.07.004] - DOI - PubMed
Wang 2017 {published data only}
Yen 2018 {published data only}
Yilmaz 2021 {published data only}
-
- Yilmaz B, Kayadibi H, Yeniova AO, Koseoglu H, Simsek Z. The age, bilirubin and albumin (ABA) index: a novel noninvasive index for predicting liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2021;33(1):e290-6. - PubMed
Additional references
Bedossa 2003
-
- Bedossa P, Dargere D, Paradis V. Sampling variability of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003;38(6):1449-57. - PubMed
Bonekamp 2009
-
- Bonekamp S, Kamel I, Solga S, Clark J. Can imaging modalities diagnose and stage hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis accurately? Journal of Hepatology 2009;50(1):17-35. - PubMed
Bravo 2001
-
- Bravo AA, Sheth SG, Chopra S. Liver biopsy. New England Journal of Medicine 2001;344(7):495-500. - PubMed
Castera 2008
-
- Castera L, Forns X, Alberti A. Non-invasive evaluation of liver fibrosis using transient elastography. Journal of Hepatology 2008;48(5):835-47. - PubMed
Castera 2009
-
- Castera L. Transient elastography and other noninvasive tests to assess hepatic fibrosis in patients with viral hepatitis. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 2009;16(5):300-14. - PubMed
Cholongitas 2006
-
- Cholongitas E, Senzolo M, Standish R, Marelli L, Quaglia A, Patch D, et al. A systematic review of the quality of liver biopsy specimens. American Journal of Clinical Pathology 2006;125(5):710-21. - PubMed
Chou 2013
-
- Chou R, Wasson N. Blood tests to diagnose fibrosis or cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a systematic review. Annals of Internal Medicine 2013;158(11):807-20. - PubMed
Colloredo 2003
-
- Colloredo G, Guido M, Sonzogni A, Leandro G. Impact of liver biopsy size on histological evaluation of chronic viral hepatitis: the smaller the sample, the milder the disease. Journal of Hepatology 2003;39(2):239-44. - PubMed
Crossan 2015
-
- Crossan C, Tsochatzis EA, Longworth L, Gurusamy K, Davidson B, Rodríguez-Perálvarez M, et al. Cost-effectiveness of non-invasive methods for assessment and monitoring of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic liver disease: systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technology Assessment 2015;19(9):1-409. - PMC - PubMed
Deeks 2023
-
- Deeks JJ, Bossuyt PM, Leeflang MM, Takwoingi Y (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy. Version 2.0 (updated July 2023). Cochrane, 2023. Available from training.cochrane.org/handbook-diagnostic-test-accuracy/current. - PMC - PubMed
Dufour 2000
-
- Dufour DR, Lott JA, Nolte FS, Gretch DR, Koff RS, Seeff LB. Diagnosis and monitoring of hepatic injury. I. Performance characteristics of laboratory tests. Clinical Chemistry 2000;46(12):2027-49. - PubMed
EASL 2015
EASL 2020
-
- Pawlotsky JM, Negro F, Aghemo A, Berenguer M, Dalgard O, Dusheiko G, et al, European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL recommendations on treatment of hepatitis C: final update of the series. Journal of Hepatology 1;73(5):1170-218. [DOI: ]
EASL 2021
-
- Berzigotti A, Tsochatzis E, Boursier J, Castera L, Cazzagon N, Friedrich-Rust M, et al, European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis – 2021 update. Journal of Hepatology 1;75(3):659-89. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.05.025] - DOI - PubMed
EASL‐ALEH 2015
Francque 2021
Glanville 2010
-
- Glanville J, Cikalo M, Crawford F, Dozier M, Lowson P. Handsearching for reports of diagnostic test accuracy studies: adding to the evidence base. In: Bero L, Montgomery P, Robinson K, Pigott T, Krause K. Bringing Evidence-Based Decision-Making to New Heights. Abstracts of the 2010 Joint Colloquium of The Cochrane and Campbell Collaborations; 2010 Oct 18-22; Keystone, USA. John Wiley & Sons; 2010. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000002] - DOI
Goodman 2007
-
- Goodman ZD. Grading and staging systems for inflammation and fibrosis in chronic liver diseases. Journal of Hepatology 1;47(4):598-607. - PubMed
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
-
- GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed 23 April 2024. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2010. Available at gradepro.org.
Greenhalgh 2005
Grigorescu 2006
-
- Grigorescu M. Noninvasive biochemical markers of liver fibrosis. Journal of Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases 2006;15(2):149-59. - PubMed
Guyatt 2011
Hanley 1982
Huwart 2008
-
- Huwart L, Sempoux C, Vicaut E, Salameh N, Annet L, Danse E, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2008;135(1):32-40. - PubMed
Ishak 1995
-
- Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L, Callea F, De Groote J, Gudat F, et al. Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. Journal of Hepatology 1995;22(6):696-9. - PubMed
Ito 2023
Kalambokis 2007
-
- Kalambokis G, Manousou P, Vibhakorn S, Marelli L, Cholongitas E, Senzolo M, et al. Transjugular liver biopsy - indications, adequacy, quality of specimens, and complications - a systematic review. Journal of Hepatology 2007;47(2):284-94. - PubMed
Knodell 1981
-
- Knodell RG, Ishak KG, Black WC, Chen TS, Craig R, Kaplowitz N, et al. Formulation and application of a numerical scoring system for assessing histological activity in asymptomatic chronic active hepatitis. Hepatology 1981;1(5):431-5. - PubMed
Li 2017
Lichtinghagen 2013
-
- Lichtinghagen R, Pietsch D, Bantel H, Manns MP, Brand K, Bahr MJ. The Enhanced Liver Fibrosis (ELF) score: normal values, influence factors and proposed cut-off values. Journal of Hepatology 2013;59(2):236-42. - PubMed
Mathes 2019
McPherson 2017
METAVIR 1996
-
- Bedossa P, Poynard T. An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Hepatology 1996;24(2):289-93. - PubMed
Nguyen 2011
-
- Nguyen D, Talwalkar JA. Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2011;53(6):2107-10. - PubMed
Pavlov 2015a
-
- Pavlov CS, Casazza G, Nikolova D, Tsochatzis E, Ivashkin VT, Gluud C. FibroTest, transient elastography method, and combined FibroTest and transient elastography method for diagnosis of severe hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis in adults with chronic hepatitis C. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016, Issue 7. Art. No: CD012291. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012291] - DOI
Pavlov 2015b
-
- Pavlov CS, Casazza G, Nikolova D, Tsochatzis E, Burroughs AK, Ivashkin VT, et al. Transient elastography for diagnosis of stages of hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis in people with alcoholic liver disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 1. Art. No: CD010542. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010542.pub2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Poynard 2011
Saadoun 2006
Scheuer 1991
-
- Scheuer PJ. Classification of chronic viral hepatitis: a need for reassessment. Journal of Hepatology 1991;13(3):372-4. - PubMed
Sebastiani 2006
Shah 2009
Shaheen 2008
Smith 2009
-
- Smith JO, Sterling RK. Systematic review: non-invasive methods of fibrosis analysis in chronic hepatitis C. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2009;30(6):557-76. - PubMed
Standish 2006
Tsochatzis 2014
-
- Tsochatzis EA, Bosch J, Burroughs AK. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet 2014;383(9930):1749-61. - PubMed
Whiting 2011
-
- Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Annals of Internal Medicine 2011;155(8):529-36. - PubMed
Xiao 2015
-
- Xiao G, Yang J, Yan L. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index and fibrosis-4 index for detecting liver fibrosis in adult patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2015;61(1):292-302. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

