Targeted next-generation sequencing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from patient samples: lessons learned from high drug-resistant burden clinical settings in Bangladesh
- PMID: 39136526
- PMCID: PMC11348811
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2024.2392656
Targeted next-generation sequencing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from patient samples: lessons learned from high drug-resistant burden clinical settings in Bangladesh
Abstract
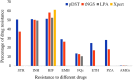
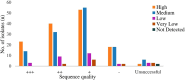
Lack of appropriate early diagnostic tools for drug-resistant tuberculosis (DR-TB) and their incomplete drug susceptibility testing (DST) profiling is concerning for TB disease control. Existing methods, such as phenotypic DST (pDST), are time-consuming, while Xpert MTB/RIF (Xpert) and line probe assay (LPA) are limited to detecting resistance to few drugs. Targeted next-generation sequencing (tNGS) has been recently approved by WHO as an alternative approach for rapid and comprehensive DST. We aimed to investigate the performance and feasibility of tNGS for detecting DR-TB directly from clinical samples in Bangladesh. pDST, LPA and tNGS were performed among 264 sputum samples, either rifampicin-resistant (RR) or rifampicin-sensitive (RS) TB cases confirmed by Xpert assay. Resistotypes of tNGS were compared with pDST, LPA and composite reference standard (CRS, resistant if either pDST or LPA showed a resistant result). tNGS results revealed higher sensitivities for rifampicin (RIF) (99.3%), isoniazid (INH) (96.3%), fluoroquinolones (FQs) (94.4%), and aminoglycosides (AMGs) (100%) but comparatively lower for ethambutol (76.6%), streptomycin (68.7%), ethionamide (56.0%) and pyrazinamide (50.7%) when compared with pDST. The sensitivities of tNGS for INH, RIF, FQs and AMGs were 93.0%, 96.6%, 90.9%, and 100%, respectively and the specificities ranged from 91.3 to 100% when compared with CRS. This proof of concept study, conducted in a high-burden setting demonstrated that tNGS is a valuable tool for identifying DR-TB directly from the clinical specimens. Its feasibility in our laboratory suggests potential implementation and moving tNGS from research settings into clinical settings.
Keywords: Targeted next-generation sequencing; diagnostic performance; drug-resistant TB; feasibility; lineage; mutation; phenotypic drug susceptibility testing.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Viney K, Linh NN, Gegia M, et al. New definitions of pre-extensively and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis: update from the World Health Organization. Eur Respiratory Soc; 2021. - PubMed
-
- Report WGT. Global Tuberculosis Report 2023; 2023.
-
- World Health Organization. WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Module 4: treatment-drug-resistant tuberculosis treatment, 2022 update. World Health Organization; 2022. - PubMed
-
- Lifescience H. GenoType MTBDRplus VER 2.0: Molecular genetic assay for identification of the M. tuberculosis complex and its resistance to rifampicin and isoniazid from clinical specimens and cultivated samples. Nehren: Hain Lifescience GmbH; 2012.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
