Integrative Multiomic Profiling of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer for Identifying Suitable Therapies
- PMID: 39136550
- PMCID: PMC11474168
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-1242
Integrative Multiomic Profiling of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer for Identifying Suitable Therapies
Abstract
Purpose: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a heterogeneous disease that carries the poorest prognosis of all breast cancers. Although novel TNBC therapies in development are frequently targeted toward tumors carrying a specific genomic, transcriptomic, or protein biomarker, it is poorly understood how these biomarkers are correlated.
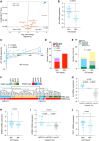
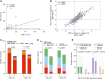
Experimental design: To better understand the molecular features of TNBC and their correlation with one another, we performed multimodal profiling on a cohort of 95 TNBC. Our approach involved quantifying tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes through hematoxylin and eosin staining, assessing the abundance of retinoblastoma, androgen receptor, and PDL1 proteins through IHC, and carrying out transcriptomic profiling using the NanoString BC360 platform, targeted DNA sequencing on a subset of cases, as well as evaluating associations with overall survival.
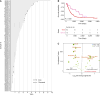
Results: Levels of RB1 mRNA and RB proteins are better correlated with markers of retinoblastoma functionality than RB1 mutational status. Luminal androgen receptor tumors clustered into two groups with transcriptomes that cluster with either basal or mesenchymal tumors. Tumors classified as PDL1-positive by the presence of immune or tumor cells showed similar biological characteristics. HER2-low TNBC showed no distinct biological phenotype when compared with HER2-zero. The majority of TNBC were classified as basal or HER2-enriched by PAM50, the latter showing significantly improved overall survival.
Conclusions: Our study contributes new insights into biomarker utility for identifying suitable TNBC therapies and the intercorrelations between genomic, transcriptomic, protein, and cellular biomarkers. Additionally, our rich data resource can be used by other researchers to explore the interplay between DNA, RNA, and protein biomarkers in TNBC.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
S.E. Church reports other support from NanoString Technologies outside the submitted work. K. North reports employment with NanoString Technologies Inc when completing this work. E.T. Richardson reports personal fees and nonfinancial support from Merck & Co, Inc and grants from AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. V. Attaya reports personal fees from Olema Oncology outside the submitted work. N.U. Lin reports grants from Genentech, Zion Pharmaceuticals, and Merck; grants and personal fees from Pfizer/SeaGen, AstraZeneca, and Olema Pharmaceuticals; and personal fees from Stemline/Menarini, Artera Inc, Daiichi Sankyo, Blueprint Medicines, and Janssen outside the submitted work. E.A. Mittendorf reports other support from AstraZeneca, BioNTech, Merck, Moderna, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Gilead, and American Society of Clinical Oncology; nonfinancial support from BMS and Roche/Genentech; and grants from Roche/Genentech and Susan G. Komen outside the submitted work. S.M. Tolaney reports grants from Eli Lilly during the conduct of the study as well as grants and personal fees from Genentech/Roche, Merck, Pfizer, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, AstraZeneca, Gilead, Seattle Genetics, and Jazz Pharmaceuticals; grants from Exelixis, NanoString Technologies, and OncoPep; and personal fees from Eli Lilly, Sanofi, CytomX Therapeutics, Daiichi Sankyo, OncXerna, Zymeworks, Zentalis, Blueprint Medicines, Reveal Genomics, ARC Therapeutics, Infinity Therapeutics, Sumitovant Biopharma, Umoja Biopharma, Artios Pharma, Menarini/Stemline, Aadi Bio, Bayer, Incyte Corp, Natera, Tango Therapeutics, Systimmune, eFFECTOR, Hengrui USA, Cullinan Oncology, Circle Pharma, Arvinas, BioNTech, and Johnson & Johnson outside the submitted work. S. Goel reports grants from Eli Lilly during the conduct of the study as well as grants from Gi Therapeutics and Incyclix Bio and personal fees from Pfizer, Novartis, Regor Pharmaceuticals, and Beigene outside the submitted work. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures


References
-
- Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2000;406:747–52. - PubMed
-
- Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM, Kahn HK, Sawka CA, et al. Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:4429–34. - PubMed
-
- Carey LA, Dees EC, Sawyer L, Gatti L, Moore DT, Collichio F, et al. The triple negative paradox: primary tumor chemosensitivity of breast cancer subtypes. Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:2329–34. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin 2023;73:17–48. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

