Genetic effects on the skin methylome in healthy older twins
- PMID: 39137780
- PMCID: PMC11393713
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2024.07.010
Genetic effects on the skin methylome in healthy older twins
Abstract
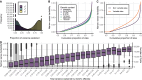
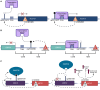
Whole-skin DNA methylation variation has been implicated in several diseases, including melanoma, but its genetic basis has not yet been fully characterized. Using bulk skin tissue samples from 414 healthy female UK twins, we performed twin-based heritability and methylation quantitative trait loci (meQTL) analyses for >400,000 DNA methylation sites. We find that the human skin DNA methylome is on average less heritable than previously estimated in blood and other tissues (mean heritability: 10.02%). meQTL analysis identified local genetic effects influencing DNA methylation at 18.8% (76,442) of tested CpG sites, as well as 1,775 CpG sites associated with at least one distal genetic variant. As a functional follow-up, we performed skin expression QTL (eQTL) analyses in a partially overlapping sample of 604 female twins. Colocalization analysis identified over 3,500 shared genetic effects affecting thousands of CpG sites (10,067) and genes (4,475). Mediation analysis of putative colocalized gene-CpG pairs identified 114 genes with evidence for eQTL effects being mediated by DNA methylation in skin, including in genes implicating skin disease such as ALOX12 and CSPG4. We further explored the relevance of skin meQTLs to skin disease and found that skin meQTLs and CpGs under genetic influence were enriched for multiple skin-related genome-wide and epigenome-wide association signals, including for melanoma and psoriasis. Our findings give insights into the regulatory landscape of epigenomic variation in skin.
Keywords: DNA methylation; QTLs; gene expression; heritability; skin.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests DG is an employee of Unilever.
Figures



References
-
- Van Dongen J., Nivard M.G., Willemsen G., Hottenga J.-J., Helmer Q., Dolan C.V., Ehli E.A., Davies G.E., van Iterson M., Breeze C.E., et al. Genetic and Environmental Influences Interact with Age and Sex in Shaping the Human Methylome. Nat. Commun. 2016;7 doi: 10.1038/ncomms11115. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Min J.L., Hemani G., Hannon E., Dekkers K.F., Castillo-Fernandez J., Luijk R., Carnero-Montoro E., Lawson D.J., Burrows K., Suderman M., et al. Genomic and Phenotypic Insights from an Atlas of Genetic Effects on DNA Methylation. Nat. Genet. 2021;53:1311–1321. doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00923-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang T., Choi J., Dilshat R., Einarsdóttir B.Ó., Kovacs M.A., Xu M., Malasky M., Chowdhury S., Jones K., Bishop D.T., et al. Cell-Type-Specific meQTLs Extend Melanoma GWAS Annotation beyond eQTLs and Inform Melanocyte Gene-Regulatory Mechanisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2021;108:1631–1646. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.06.018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hawe J.S., Wilson R., Schmid K.T., Zhou L., Lakshmanan L.N., Lehne B.C., Kühnel B., Scott W.R., Wielscher M., Yew Y.W., et al. Genetic Variation Influencing DNA Methylation Provides Insights into Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Genomic Function. Nat. Genet. 2022;54:18–29. doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00969-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

