M2-like tumor-associated macrophage-secreted CCL2 facilitates gallbladder cancer stemness and metastasis
- PMID: 39138521
- PMCID: PMC11320879
- DOI: 10.1186/s40164-024-00550-2
M2-like tumor-associated macrophage-secreted CCL2 facilitates gallbladder cancer stemness and metastasis
Abstract
Background: The predominant immune cells in solid tumors are M2-like tumor-associated macrophages (M2-like TAMs), which significantly impact the promotion of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in tumors, enhancing stemness and facilitating tumor invasion and metastasis. However, the contribution of M2-like TAMs to tumor progression in gallbladder cancer (GBC) is partially known.
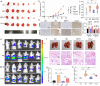
Methods: Immunohistochemistry was used to evaluate the expression of M2-like TAMs and cancer stem cell (CSC) markers in 24 pairs of GBC and adjacent noncancerous tissues from patients with GBC. Subsequently, GBC cells and M2-like TAMs were co-cultured to examine the expression of CSC markers, EMT markers, and migratory behavior. Proteomics was performed on the culture supernatant of M2-like TAMs. The mechanisms underlying the induction of EMT, stemness, and metastasis in GBC by M2-like TAMs were elucidated using proteomics and transcriptomics. GBC cells were co-cultured with undifferentiated macrophages (M0) and analyzed. The therapeutic effect of gemcitabine combined with a chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 2 (CCR2) antagonist on GBC was observed in vivo.
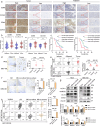
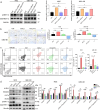
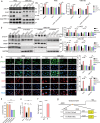
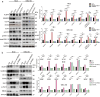
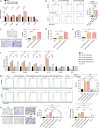
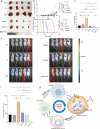
Results: The expression levels of CD68 and CD163 in M2-like TAMs and CD44 and CD133 in gallbladder cancer stem cells (GBCSCs) were increased and positively correlated in GBC tissues compared with those in neighboring noncancerous tissues. M2-like TAMs secreted a significant amount of chemotactic cytokine ligand 2 (CCL2), which activated the MEK/extracellular regulated protein kinase (ERK) pathway and enhanced SNAIL expression after binding to the receptor CCR2 on GBC cells. Activation of the ERK pathway caused nuclear translocation of ELK1, which subsequently led to increased SNAIL expression. GBCSCs mediated the recruitment and polarization of M0 into M2-like TAMs within the GBC microenvironment via CCL2 secretion. In the murine models, the combination of a CCR2 antagonist and gemcitabine efficiently inhibited the growth of subcutaneous tumors in GBC.
Conclusions: The interaction between M2-like TAMs and GBC cells is mediated by the chemokine CCL2, which activates the MEK/ERK/ELK1/SNAIL pathway in GBC cells, promoting EMT, stemness, and metastasis. A combination of a CCR2 inhibitor and gemcitabine effectively suppressed the growth of subcutaneous tumors. Consequently, our study identified promising therapeutic targets and strategies for treating GBC.
Keywords: CCL2; Cancer stem cells; Epithelial-mesenchymal transformation; Gallbladder cancer; M2-like tumor-associated macrophage.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tumor-associated macrophages promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the cancer stem cell properties in triple-negative breast cancer through CCL2/AKT/β-catenin signaling.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Jun 17;20(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00888-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 35715860 Free PMC article.
-
M2-like tumor-associated macrophages-secreted EGF promotes epithelial ovarian cancer metastasis via activating EGFR-ERK signaling and suppressing lncRNA LIMT expression.Cancer Biol Ther. 2019;20(7):956-966. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1564567. Epub 2019 May 7. Cancer Biol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31062668 Free PMC article.
-
Zoledronic acid inhibits thyroid cancer stemness and metastasis by repressing M2-like tumor-associated macrophages induced Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Life Sci. 2020 Sep 1;256:117925. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117925. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32522570
-
A narrative review of tumor-associated macrophages in lung cancer: regulation of macrophage polarization and therapeutic implications.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021 Apr;10(4):1889-1916. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-1241. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34012800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting tumor-associated macrophages in the tumor microenvironment.Oncol Lett. 2020 Nov;20(5):234. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12097. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32968456 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Lymph Node Metastasis in Gallbladder Cancer: Insights into the Tumor Microenvironment.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 4;13(6):1372. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061372. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophages at the Crossroads of Chronic Stress and Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 16;26(14):6838. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146838. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gold and Silver Nanoparticles Efficiently Modulate the Crosstalk Between Macrophages and Cancer Cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Apr 15;20:4777-4802. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S508171. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40255669 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
- 2021QH2026/Startup Fund for Scientific Research, Fujian Medical University
- 2019QH1044/Startup Fund for Scientific Research, Fujian Medical University
- 2020Y9075/Science and Technology Innovation Joint Foundation of Fujian Province
- [2021]76/High-Level Medical Care Construction Foundation of Fujian Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

