Causal effects of omega-6 and LDL-C on androgenetic alopecia: A Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 39138832
- PMCID: PMC11322220
- DOI: 10.1111/srt.70000
Causal effects of omega-6 and LDL-C on androgenetic alopecia: A Mendelian randomization study
Retraction in
-
RETRACTION: Causal Effects of Omega-6 and LDL-C on Androgenetic Alopecia: A Mendelian Randomization Study.Skin Res Technol. 2025 Jun;31(6):e70195. doi: 10.1111/srt.70195. Skin Res Technol. 2025. PMID: 40536146 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Increasing studies have reported a causal relationship between androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and lipid-related metabolites. However, the relationships between HDL-C, LDL-C, Omega-6, and Omega-3 with AGA remain unclear. Some research findings are even contradictory. Therefore, we designed this study to explore this issue.
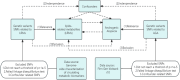
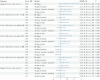
Methods: In this study, we selected seven exposure factors, screened SNPs with significant associations, removed linkage disequilibrium and weak instrumental variables, and conducted bidirectional MR analysis.
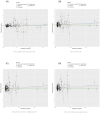
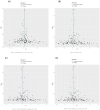
Results: The study found that omega-6 and LDL-C, especially total cholesterol in medium LDL and total cholesterol in small LDL, are risk factors for the occurrence of androgenetic alopecia.
Conclusion: In summary, we found that various lipid-related metabolites have a causal relationship with the occurrence of androgenetic alopecia, providing new insights into the pathogenesis of androgenetic alopecia and offering references for clinical treatment of androgenetic alopecia.
Keywords: LDL‐C; Mendelian randomization; Omega‐6; androgenic alopecia.
© 2024 The Author(s). Skin Research and Technology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ho CH, Sood T, Zito PM. Androgenetic Alopecia. StatPearls Publishing,; 2023. - PubMed
-
- Phillips TG, Slomiany WP, Allison R. Hair loss: common causes and treatment. Am Fam Physician. 2017;96(6):371‐378. - PubMed
-
- Braun N, Heinrich U. What can complex dietary supplements do for hair loss and how can it be validly measured—a review. Appl Sci. 2020;10(14): 4996. 10.3390/app10144996 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

