Robotic management of urinary fistula
- PMID: 39139533
- PMCID: PMC11318412
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajur.2023.11.002
Robotic management of urinary fistula
Abstract
Objectives: To highlight critical preoperative and intraoperative considerations in approaching fistula repair robotically.
Methods: A search of the literature was conducted to identify relevant articles pertaining to robotic management of urinary fistulae.
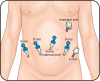
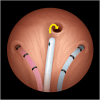
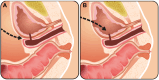
Results: Fistulae of the genitourinary tract can be a challenging dilemma for urologists, as definitive management may require surgical intervention. Pathogenesis of both enteric and non-enteric fistulae are multifactorial, and successful repair hinges on the meticulous perioperative evaluation, planning, and execution. Traditional open techniques can subject patients to increased morbidity and prolonged hospitalizations. Since its introduction, the robotic surgical platform has continued to expand its indications. Its three-dimensional visualization and tremor free wristed instrument movements have made the robotic platform an attractive option for genitourinary fistula reconstruction.
Conclusion: Robotic management of complex urinary fistulae is feasible in expert hands; more studies are needed to define its role in the treatment algorithm of this devastating conditions.
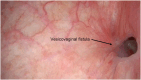
Keywords: Fistula; Rectourethral; Rectovesical; Robotic surgery; Vesicovaginal.
© 2024 Editorial Office of Asian Journal of Urology. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fistula Merriam-webster. https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/fistula
-
- Angioli R., Penalver M., Muzii L., Mendez L., Mirhashemi R., Bellati F., et al. Guidelines of how to manage vesicovaginal fistula. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2003;48:295–304. - PubMed
-
- Vangeenderhuysen C., Prual A., Ould el Joud D. Obstetric fistulae: incidence estimates for sub-Saharan Africa. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2001;73:65–66. - PubMed
-
- Rangel E., Perez L.C., Polotti C.F. In: Urinary fistula. Sotelo R., Polotti C.F., Arriaga J., editors. Springer International Publishing; Switzerland: 2022. General considerations. p3.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

