The genome sequence of the Crescent Groundling, Teleiodes luculella (Hübner, 1813)
- PMID: 39139615
- PMCID: PMC11319900
- DOI: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.21090.1
The genome sequence of the Crescent Groundling, Teleiodes luculella (Hübner, 1813)
Abstract
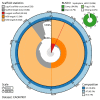
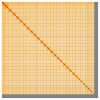
We present a genome assembly from an individual male Teleiodes luculella (the Crescent Groundling; Arthropoda; Insecta; Lepidoptera; Gelechiidae). The genome sequence is 454.5 megabases in span. Most of the assembly is scaffolded into 30 chromosomal pseudomolecules, including the Z sex chromosome. The mitochondrial genome has also been assembled and is 15.32 kilobases in length. Gene annotation of this assembly on Ensembl identified 19,943 protein coding genes.
Keywords: Lepidoptera; Teleiodes luculella; chromosomal; crescent groundling; genome sequence.
Copyright: © 2024 Boyes D et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The genome sequence of the Elm Groundling moth, Carpatolechia fugitivella (Zeller, 1839).Wellcome Open Res. 2024 Apr 23;9:211. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.21267.1. eCollection 2024. Wellcome Open Res. 2024. PMID: 39139614 Free PMC article.
-
The genome sequence of the Dotted Grey Groundling, Athrips mouffetella (Linnaeus, 1758).Wellcome Open Res. 2024 Feb 19;9:42. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.20840.1. eCollection 2024. Wellcome Open Res. 2024. PMID: 39015611 Free PMC article.
-
The genome sequence of the Olive Crescent, Trisateles emortualis (Denis & Schiffermüller, 1775).Wellcome Open Res. 2024 Apr 8;9:178. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.20836.1. eCollection 2024. Wellcome Open Res. 2024. PMID: 40012989 Free PMC article.
-
The genome sequence of the Green-brindled Crescent, Allophyes oxyacanthae (Linnaeus, 1758).Wellcome Open Res. 2023 Feb 3;8:53. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.18935.1. eCollection 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2023. PMID: 39148947 Free PMC article.
-
The genome sequence of the Crescent Plume, Marasmarcha lunaedactyla (Haworth, 1811).Wellcome Open Res. 2023 Oct 6;8:431. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.20107.1. eCollection 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2023. PMID: 39359327 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bates A, Clayton-Lucey I, Howard C: Sanger Tree of Life HMW DNA Fragmentation: Diagenode Megaruptor® 3 for LI PacBio. Protocols.Io. 2023. 10.17504/Protocols.Io.81wgbxzq3lpk/V1 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

